|
Pine Forest Fires
Pine forests range from dense tree stands to sparce tree stands. The
accessory fuels range from other tree species and shrubs to primarily
grasses. The subsections that follow are only a partial list of common pine
ecosystems and a fire may include a number of different ecosystems as it
grows. The assemblages here are provided as an aid in characterizing the
particles generated by the fire.
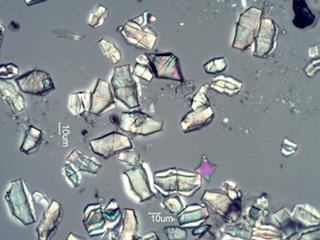
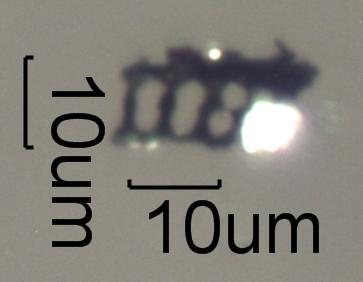
The most diagnostic single particle generated by pine forest fires anywhere
in the world is the bipyramidal tablet of calcium oxalate shown below.
These crystals are concentrated in the needles and bark of pine trees and
are a very common particle in the plume from a pine forest fire.



Pine/Shrub Fires
Pine/Shrub forest in the Northwest US (Washington, Idaho, Western Montana,
Oregon) typically consist of Ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) with some
Douglas fir (PseudoTsuga menziesii), Grand fir (Abies grandis), and Tamarac
(Larix occidentalis). The shrub layer includes snowberry (Symphoricarpos
albus), service berry (Amelanchier alnifolia), wild cherry (Prunus
virginiana), ocean spray (Holodiscus discolor), wild rose (Rosa), mallow
ninebark
(Physocarpus malvaceus), and spiraea (Spiraea). In some areas antelope bush
(Purshia tridentata) is a dominant shrub. Grasses are common in the
understory.
Pine/Shrub forest in Wyoming and South Dakota includes black hills spruce
(Picea glauca), rocky mountain juniper (Juniperus scopulorum), bur oak
(Quercus macrocarpa), Quaking aspen (Populus trem, paper birch (Betula
papyrifera)
Pine/Shrub forest in the California White fir (Abies concolor), incense
cedar, Douglas fir, Black oak (Quercus kelloggii), and western
juniper (Juniperus occidentalis)
Pine/Shrub forests in Arizona and New Mexico include White fir, Douglas fir,
Quaking aspen, shrub live oak (Quercis turbinella), and Junipers at
higher elevations.
Pine/Shrub forests in Utah and Colorado Douglas fir, blue spruce (Picea
pungens), and quaking aspen (Populus tremuloides). Shrubs include Gambel
oak, mountain mahogany, and sagebrush
. . . Phytoliths
. . . Douglas Fir (PseudoTsuga menziesii) Needles and Bark
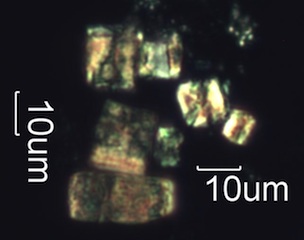
Small cubes and square prisms are characteristic of Douglas fir bark and
needles.




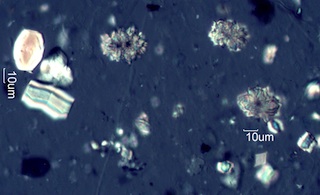
. . . Snowberry (Symphoricarpus albus)
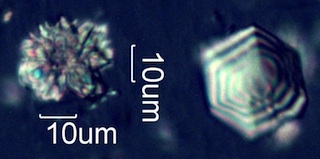
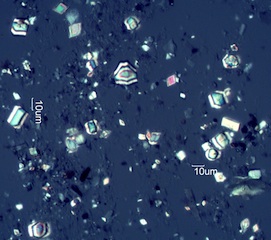
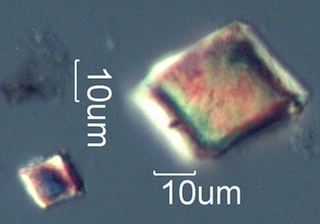
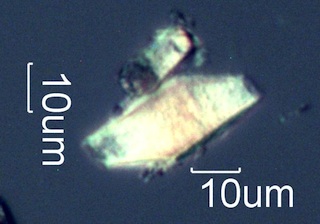
. . . Service Berry (Amelanchier alnifolia) [Washington, Northern Oregon,
Northern Idaho, Western Montana, South Dakota]
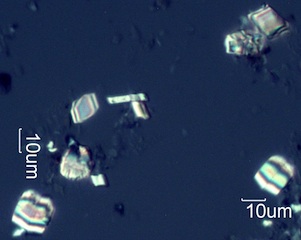
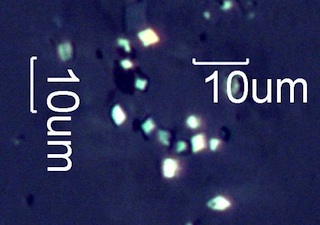
. . . Ocean Spray (Holodiscus discolor)
The common form of calcium oxalate here is druse rosettes in the bark and
twigs and diamonds in the dried flower tufts. Both are found in the plume
of fires where this is a common shrub.

. . . Wild Rose (Rosa sp.)
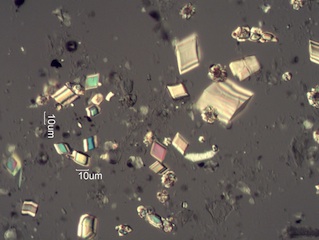
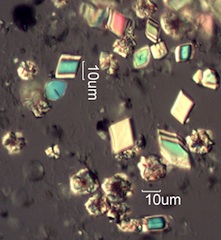
. . . Hawthorn (Crataegus douglasii)
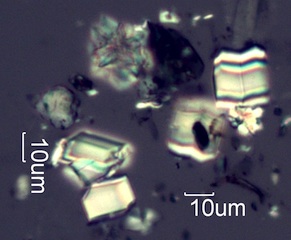
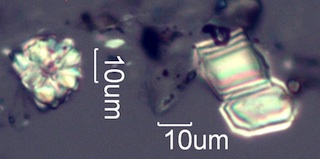
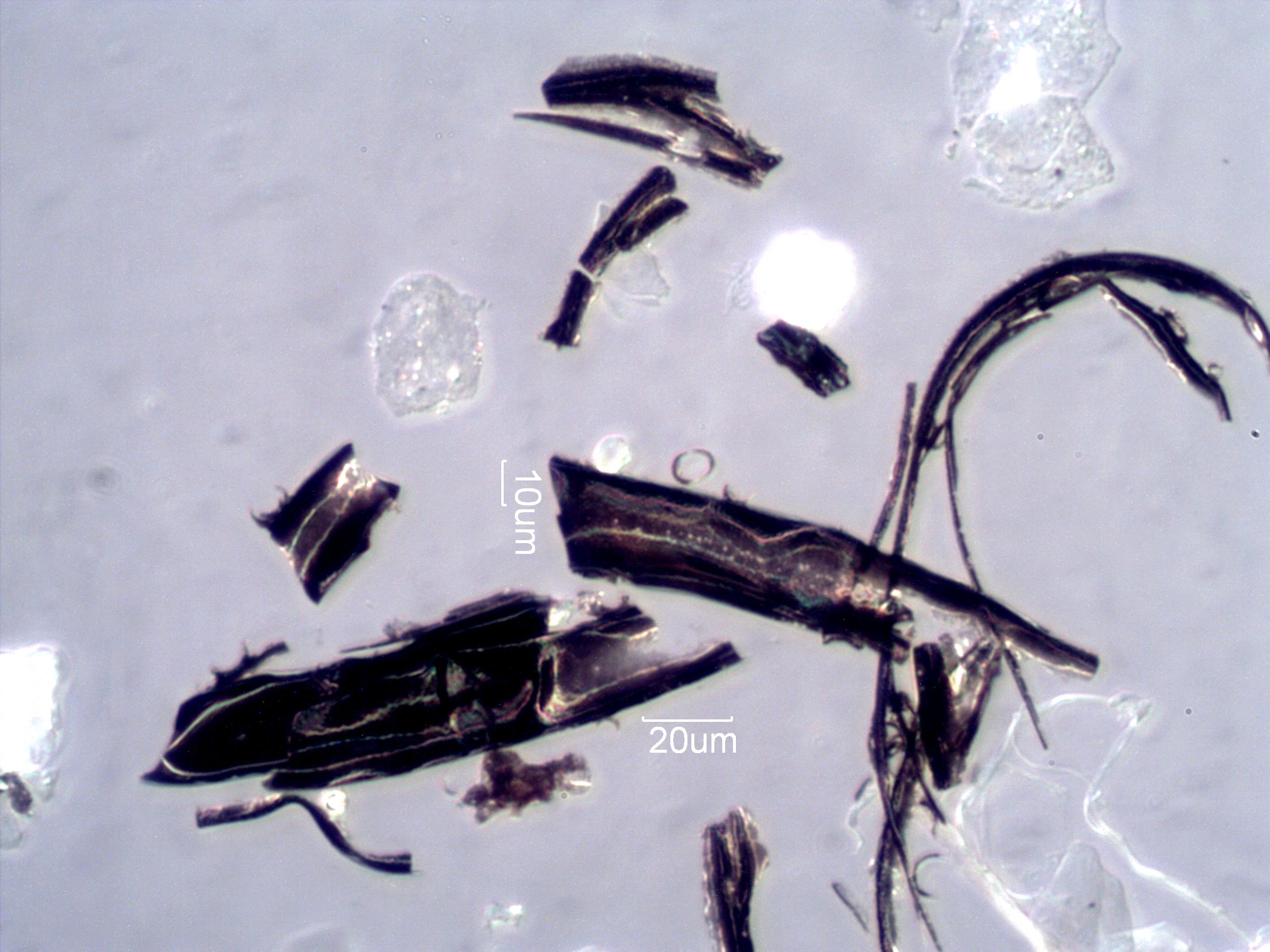
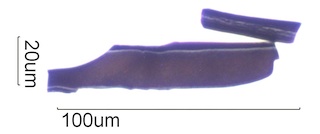
. . . Charred Wood
. . . Douglas Fir Charred Wood
Pine/Grass Fires
Chaparrell Fires
. . . California Chaparrell Fires
Shrub Oaks (Blue, Live, Gamble,), Coyote Brush (Baccharis pilularis),
Sagebrush, Fairy Duster (Calliandra eriophylla), French Broom (Cytisus
monspessulanus),
Protea, Lebanon cedar, Manzanita (Arctostaphylos manzanita), Mountain
Mahogany (Cerocarpus montanus), Olive Tree (Olea europaea), Lemonade Sumac
(Rhus integrifolia), Buckwheats (Eriogonum fasciculatum), Cleveland and
black sage (Salvia clevelandii and melifera), Redshanks (Adenostoma
sparsifolium),
Ceanothus (Ceanothus spp.), Toyon (Heteromeles arbutifolia)
. . . Scrub Live Oak (Quercus turbinella)
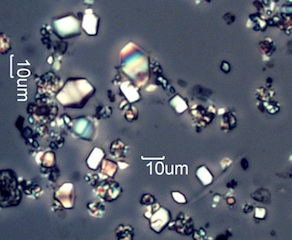
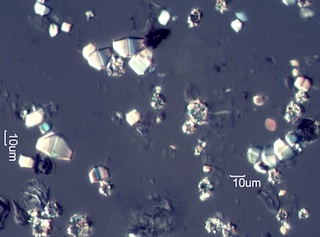
. . . Lemonade Sumac (Rhus integrifolia)

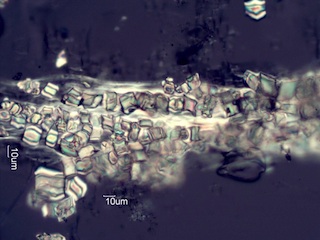 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chaparral
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chaparral
. . . California and Arizona Desert Fires
. . . Brittlebush (Encelia farinosa)

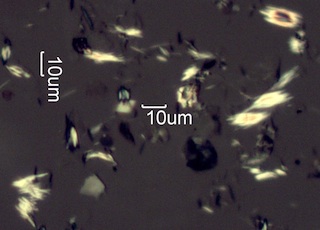
Creosotebush (Larrea tridentata)

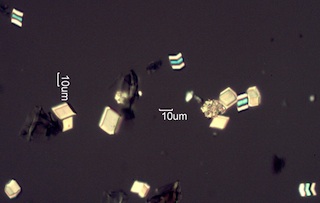
. . . Arizona Chaparrell Fires
Plains lovegrass (Eragrostis intermedia), Smoke Tree (Dalea spinosa), Verbena
(Glandularia spp.), Blue Grama (Bouteloua ), Beggarticks
(Bidens spp.), Scrub Oak (Quercus spp.), Deergrass (Muhlenbergia rigens),
Shrubby Deervetch (Lotus rigidus),
. . . Arizona Sycamore (Platanus wrightii)
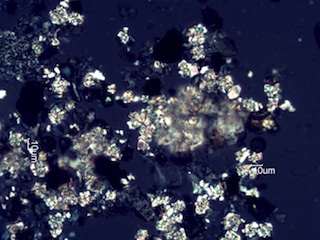
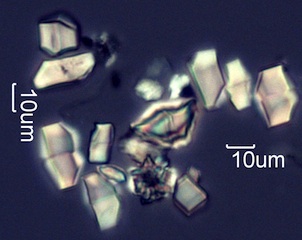
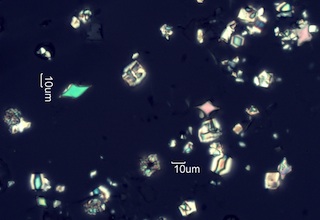
Sage/Grass Fires
Artemisia tridentata and tripartita cover large areas of Eastern Washington,
Eastern Oregon, Southern Idaho, Eastern Montana, and most of Nevada and
Wyoming.
Charred Wood






|