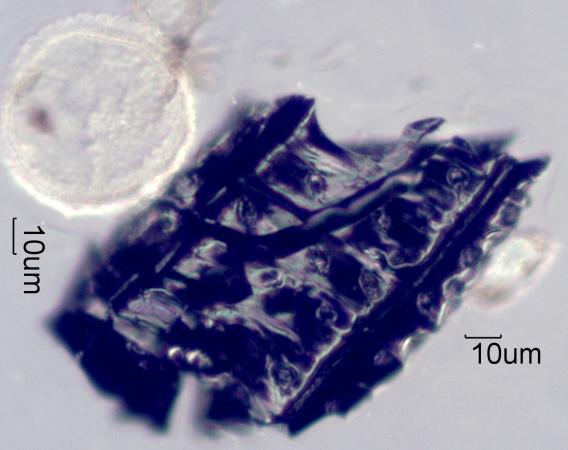
Charred Wood from a House Fire
This is a piece of charred Douglas fir showing the
cross-field pitting. The particle at upper left is a cedar
pollen grain. This was from an environmental tapelift collected in a modern log home
after a house fire.
Transmitted Off Crossed Polarized Light and Reflected Darkfield Illumination
Definition/Function:
Charring or coking of wood tends to retain the structure of the wood. As a result the
genus or even the species of the wood can often be determined
from an examination of the structure still evident. There is a reduction in the size of
the structures of about 20% typically.
Significance in the Environment:
Many types of wood are used in a wood structure building. The studs and structural beams
in a wood building are often Douglas fir or Pine. This
wood is often the dominant type of charred wood in the burnt building. The finish woods
are generally hardwoods though Cedar and Pine are also used
as a common paneling in some regions.
Characteristic Features:
Associated Particles:
References: