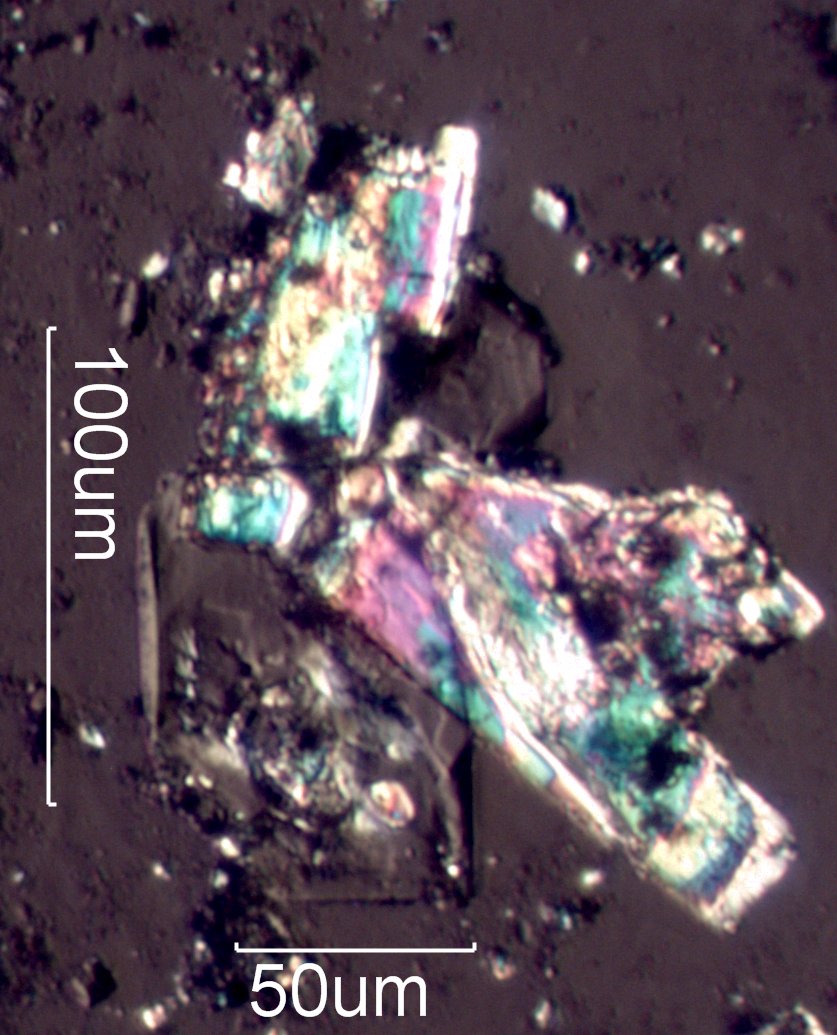
Urea and Sodium Chloride Crystals
A yellow stain near the molding on a bathroom floor was suspected to be fungal growth. This is from an environmental tapelift of the stain. The large colorful crystals seen here are urea. The darker crystals are sodium chloride. These two compounds are typically associated in a urine deposit.
Transmitted Off Crossed Circular Polarized Light
Definition/Function:
Urea is CO(NH2)2. It is excreted by mammals in the urine as a breakdown product of protein.
Significance in the Environment:
Urea is a common marker for urine stains in indoor environments. Pet related stains on floors or rodent paths are common locations associated with urea from mammalian urine.
Characteristic Features:
Urea is a colorless, optically positive, tetragonal crystal with refractive indices of 1.484 (omega) and 1.602 (epsilon).
Associated Particles:
When part of a deposit from urine it is associated with sodium chloride and other organic and inorganic salts.