Rutile
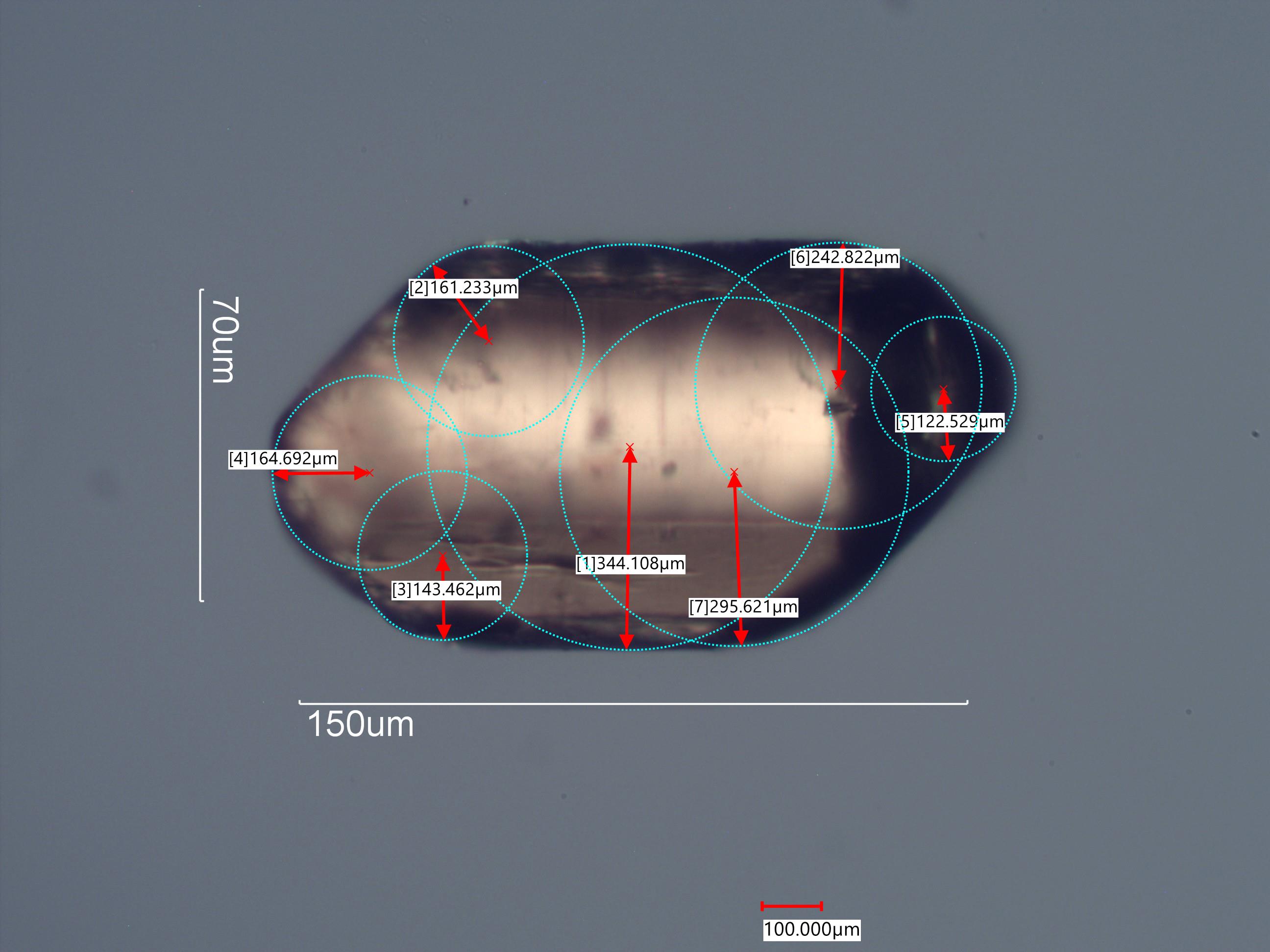
This is a rutile particle from the beach sand on Big Talbot
Island, Florida. This particle has a
roundness of 0.55 by the average radius of angles divided by the radius of the
maximum enclosed circle and 0.54 by the maximum
enclosed circle radius divided by the radius of the minimum circumscribed circle..
Transmitted Off Crossed Circular Polarized Light
Definition/Function:
Rutile is one form of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2).
Significance in the Environment:
Characteristic Features:
Rutile belongs to the tetragonal crystal system and is optically positive. Its
refractive indices are 2.605-2.613 and 2.899-2.901.
Its birefringence ranges from 0.286 to 0.296. The density of Rutile ranges from 4.23 to
5.5 grams/cc. Small grains tend to be
reddish brown to yellow. Rutile is often found in soils and sands as a well formed
crystal or as a rounded ellipse.
Associated Particles:
Rutile is common in heavy mineral sand formations.
References:
Deer, W. A., R. A. Howie, and J. Zussman, AN INTRODCUTION TO THE ROCK-FORMING MINERALS,
ISBN 0-582-30094-0, pp. 548-551, 1992.