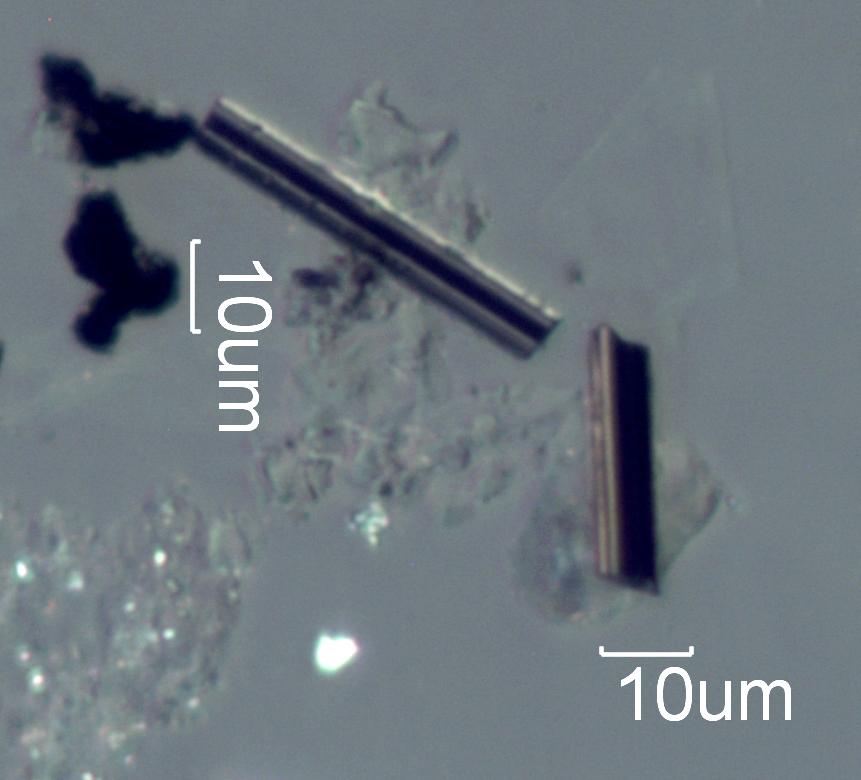
Transmitted Oblique Off Crossed Circular Polarized light and Reflected Darkfield
Illumination
Definition/Function:
Carbon fiber is a fiber produced by thermally processing a plastic or pitch-based
fiber until nearly all of the hydrogen has been removed from the
molecular structure and the carbon atoms have all bonded to other carbon atoms to
form a graphene structure. The size, orientation, and percent of
carbon involved in these graphene units determines the physical and optical
properties of the resulting carbon fiber.
Carbon fiber may be added to plastics to reduce their electrostatic properties and
prevent the development of static-electric charge. Its primary
use is in the design of high strength, light weight, composite materials. These
carbon fiber/resin composite materials are used in sporting goods
such tennis rackets, golf clubs, skis, backpack frames, bicycle frames, etc. They
are used in the bodies of automobiles, airplanes, high pressure
vessels, boat bodies, anywhere high strength and light weight may be desirable.
Carbon fiber/resin composites have been used for their unique optical
properties to make decorator objects or panels.
Significance in the Environment:
Carbon fiber is used as the stiffening, conductive, and strength fiber in a wide variety
of resin/fiber composite materials from skis to airplane
bodies. Its presence in an environment may indicate proximity to a facility that is
involved in the fabrication, refurbishment, or maintenance of
some product that includes a carbon fiber/resin component or a woven carbon fiber
conductive cloth. It may also be present as the result of
mechanical damage to a carbon fiber/resin composite material in the environment sampled.
Characteristic Features:
Carbon fibers are opaque, black, and moderately reflective, about 24% in air and a bit
less, about 18%, in a tapelift preparation. The tension on
the fiber and shrinkage during processing result in surface striations parallel to the
length of the fiber that often act as a diffraction grating
when the incidence of the reflecting beam is perpendicular to the fiber and at the
proper angle. Carbon fibers generally have a diameter between 4
and 8 micrometers. Some may be as much as 12 micrometers. Pitch precursor carbon fiber
tends to be much more variable in diameter with some of the
fibers being much larger in cross-section. A polished cross-section of a carbon
fiber/resin composite examined with reflected and/or transmitted
polarized light revels a great deal about the mechanical properties of the fibers, the
fiber resin bond, and residual stresses in the finished
composite.
Associated Particles:
Carbon fiber associated with damage to a carbon fiber/resin composite will be associated
with fragments of the resin.
References: