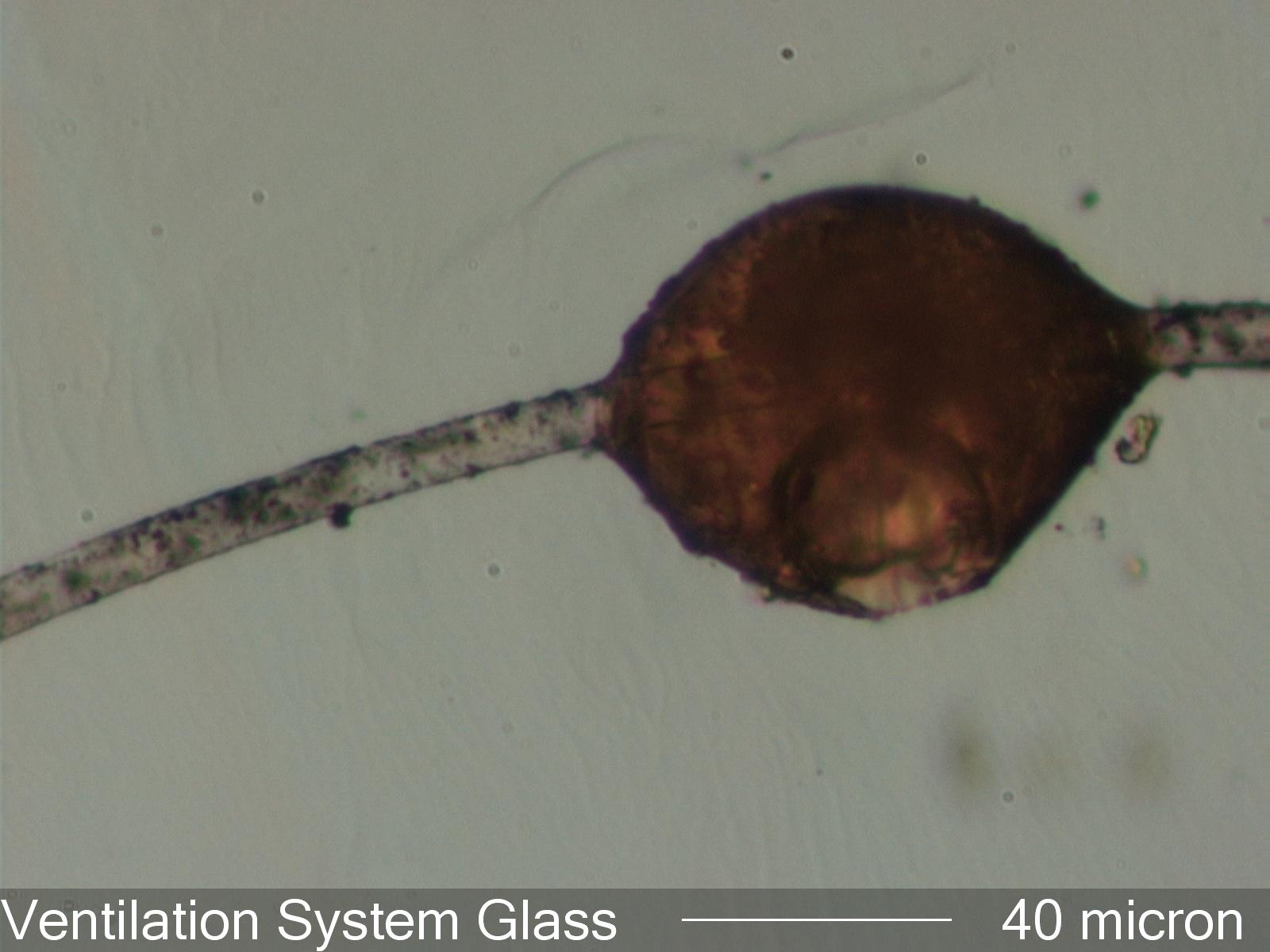
Glass Fiber from a Wall Perforation
In this case the red of the resin suggests blanket
insulation but the particle accumulation
clearly indicates exposure to a moving air stream. The size of the particles (quite
small) indicates diffusion as the
dominant deposition mechanism rather than impaction. This appears to be from a wall
perforation.
Transmitted Oblique Off Crossed Polarized Light Illumination
Definition/Function:
Significance in the Environment:
Fibers in a moving air stream collect particles from that air stream that are about the
same diameter
or smaller than the diameter of the fiber. There are a couple of different
micro-environments that can
expose glass fiber to moving air streams indoors. The most obvious is the heating,
ventilation, and cooling
system (HVAC system). Another source is glass fiber insulated walls with perforations.
All walls have per-
forations at electrical outlets, switches, or along the baseboard of the wall. Normal
"breathing" of the
wall creates the air movement and over time the glass fibers at those perforations will
become coated with
these small particles. The types of particles on the surface of the fiber can be used to
determine if the
fiber was exposed to outside air, inside air, filtered air, or recycled air with
reasonably high probability
using assembalge analysis.
In this case the red of the resin suggests blanket insulation but the particle
accumulation clearly indicates
exposure to a moving air stream. The size of the particles (quite small) indicates
diffusion as the dominant
deposition mechanism rather than impaction. This appears to be from a wall perforation.
The source of glass
glass fiber in an environment is never based on a single fiber but rather the total
glass fiber population.
There are often multiple sources of glass fiber in an environment and the glass fibers
are distributed by their
attributes into the different populations. The source of the individual populations is
then determined based on
the characteristics of all the fibers in each population. There are always some fibers
that lack sufficient asso-
ciations to place them in a population. These fibers are allocated proportionately after
the various sources are
indentified and their relative contribution to the total is determined.
Characteristic Features:
Associated Particles:
References: