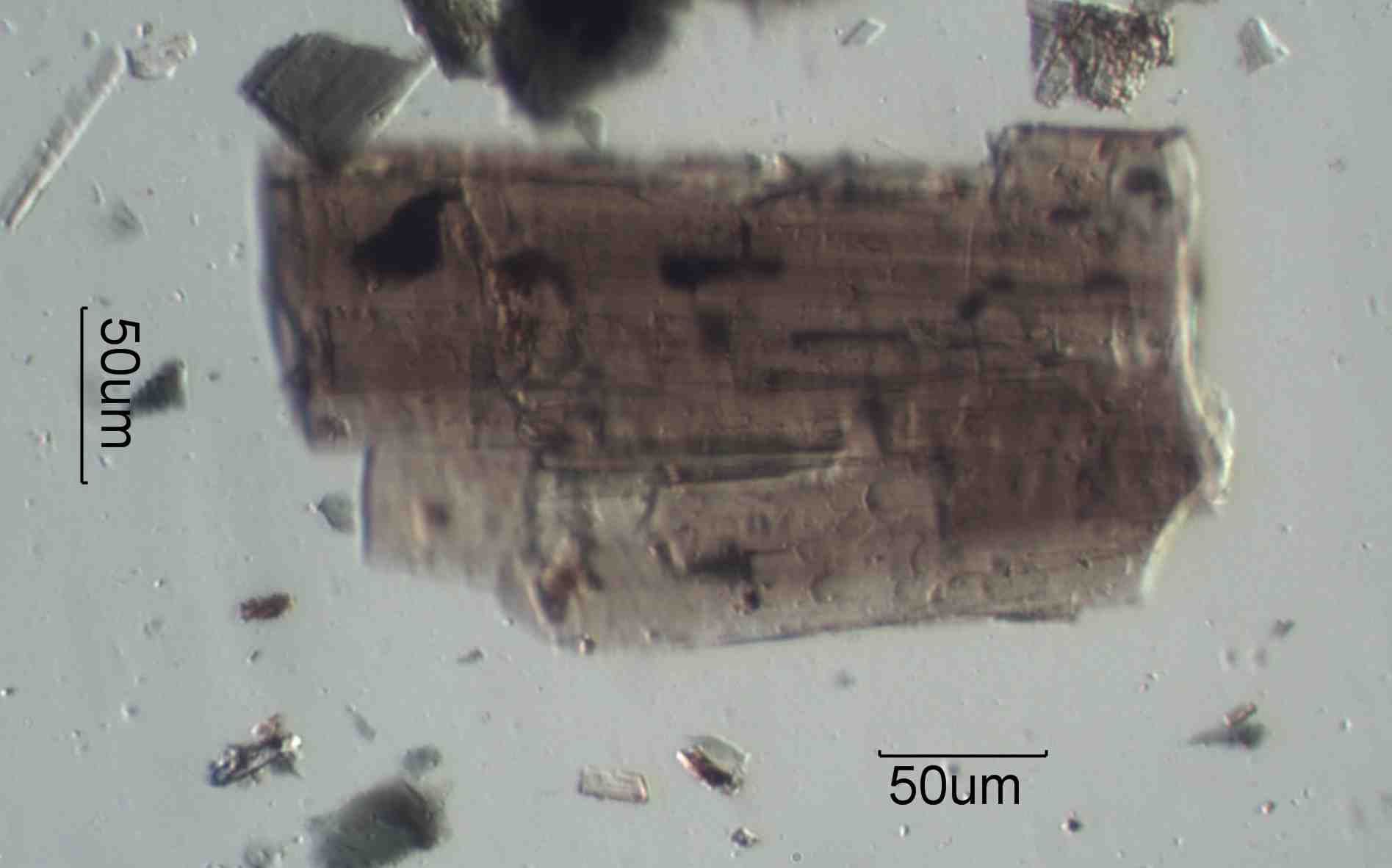
Tourmaline
This tourmaline crystal is from Lennox Creek, Washington
State. A single linear polarizing filter is oriented
parallel to the length of the crystal.
Transmitted Light with a Single Linear Polarizing Filter Oriented Parallel to the Long
Axis
Definition/Function:
Tourmaline has the general formula of
(Na,Ca)(Mg,Fe,Mn,Li,Al)3(Al,Mg,Fe)6[Si6O18](BO3)3(O,OH)3(OH,F).
It is a common mineral in some granites or metamorphic deposits.
Significance in the Environment:
Characteristic Features:
Tourmaline belongs to the trigonal crystal system and is optically negative. Its
refractive indices are 1.612-1.650 for epsilon and
1.633-1.671 for Omega. Its birefringence ranges from 0.017 to 0.035. The density of
tourmaline ranges from about 2.9 to 3.22 grams/cc.
Small grains may be colorless to black. Their pleochroism is strong if they are strongly
colored. The absorption is always strongest along
omega, the highest refractive index. The long axis of the grains tends to be the epsilon
direction.
Associated Particles:
References:
Deer, W. A., R. A. Howie, and J. Zussman, AN INTRODCUTION TO THE ROCK-FORMING MINERALS,
ISBN 0-582-30094-0, pp. 130-7, 1992.