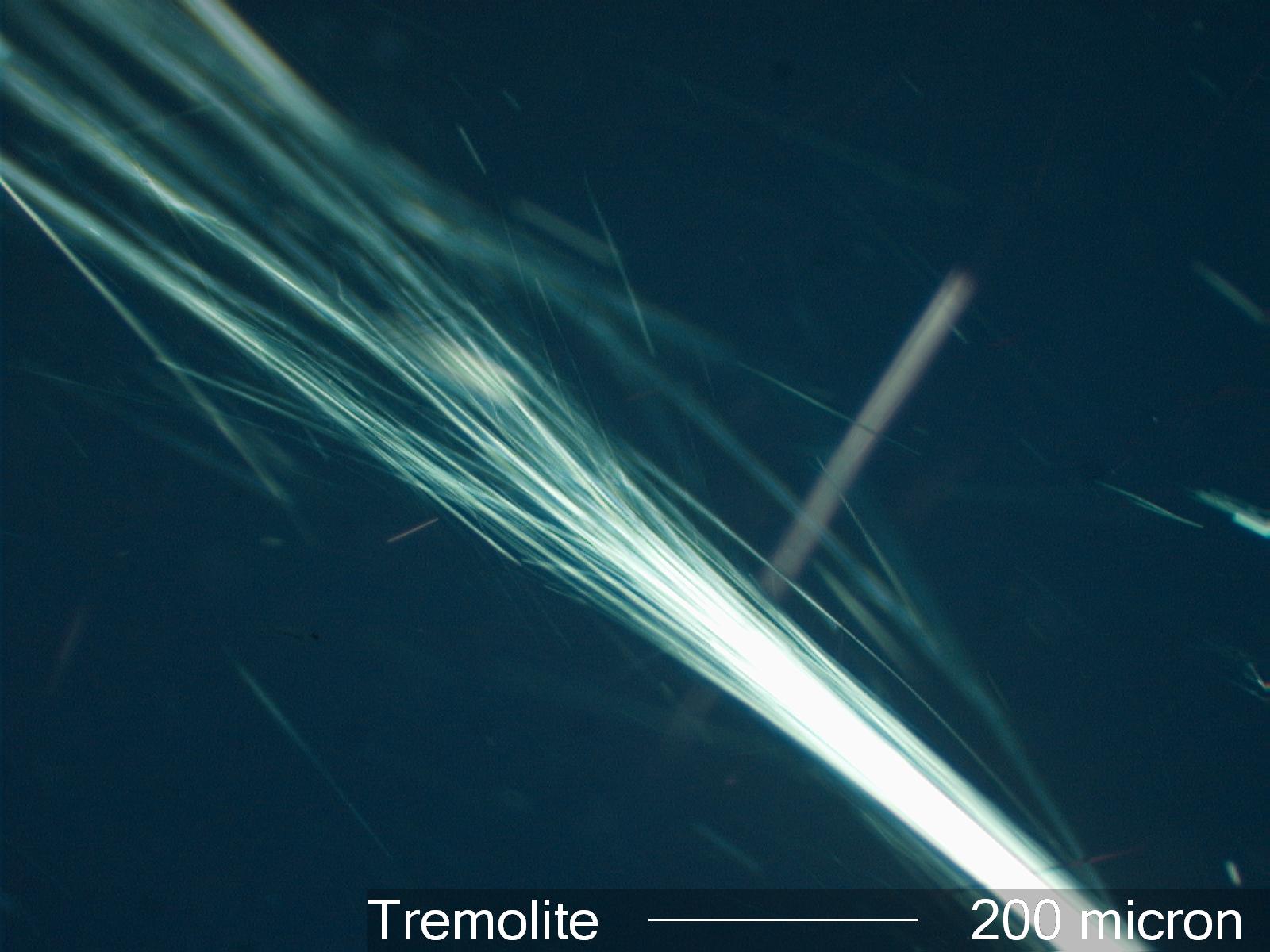
Tremolite Asbestos
Transmitted Crossed Polarized Light Illumination
2. Campbell, W.J., R.L. Blake, L.L. Brown, E.E. Cather, and J.J. Sjoberg, IC 8751; SELECTED SILICATE MINERALS AND THEIR ASBESTIFORM VARIETIES, US Dept. of the Interior, Bureau of Mines Information Circular, 1977
3. Deer, W. A., R. A. Howie, and J. Zussman, AN INTRODCUTION TO THE ROCK-FORMING MINERALS, ISBN 0-582-30094-0, pp. 22-6, 1992
4. Ledoux, R. L. (ed), SHORT COURSE IN MINERALOGICAL TECHNIQUES OF ASBESTOS DETERMINATION, Mineralogical Association of Canada, 1979.
5. Levadie, Benjamin (ed), DEFINITIONS FOR ASBESTOS AND OTHER HEALTH-RELATED SILICATES, ASTM STP 834, 1984.
6. Riordon, P. H. (ed), GEOLOGY OF ASBESTOS DEPOSITS, Society of Mining Engineers, 1981.
7. World Health Organization, ASBESTOS AND OTHER NATURAL MINERAL FIBRES, Environmental Health Criteria 53, 1986.
Definition/Function:
Tremolite asbestos is a fibrous amphibole with the chemical composition Ca2Mg 5[Si8O22](OH) 2. It is one of the more hazardous asbestos minerals.Significance in the Environment:
Tremolite had a rather limited commercial use and is encountered as an impurity in talc or vermiculite as often as it is as an intentionally added material. In materials with a significant talc content the amount of Tremolite can exceed 1%. It rarely exceeds 1% in vermiculite samples but handling vermiculite that contains Tremolite can result in respiratory exposures thousands of times higher than the allowable industrial exposure.Characteristic Features:
Tremolite has refractive indices that overlap those of Anthophyllite but Tremolite in some orientations will show oblique extinction of from 7 to 21 degrees. Anthophyllite never shows oblique extinction. Tremolite has a lower refractive index than Actinolite. Tremolite shows dispersion effects in high dispersion liquids of 1.605.Associated Particles:
As an impurity it is generally found with high concentrations of talc or in bulk vermiculite. It was used as an additive in paint and ceramics, mastics, floor tiles, acoustic tiles, and other construction materials. Because of its purity it was often used as a filter material or crucible liner in chemical analyses.References:
1. Asbestos Textile Institute, HANDBOOK OF ASBESTOS TEXTILES, 3RD EDITION, 1967.2. Campbell, W.J., R.L. Blake, L.L. Brown, E.E. Cather, and J.J. Sjoberg, IC 8751; SELECTED SILICATE MINERALS AND THEIR ASBESTIFORM VARIETIES, US Dept. of the Interior, Bureau of Mines Information Circular, 1977
3. Deer, W. A., R. A. Howie, and J. Zussman, AN INTRODCUTION TO THE ROCK-FORMING MINERALS, ISBN 0-582-30094-0, pp. 22-6, 1992
4. Ledoux, R. L. (ed), SHORT COURSE IN MINERALOGICAL TECHNIQUES OF ASBESTOS DETERMINATION, Mineralogical Association of Canada, 1979.
5. Levadie, Benjamin (ed), DEFINITIONS FOR ASBESTOS AND OTHER HEALTH-RELATED SILICATES, ASTM STP 834, 1984.
6. Riordon, P. H. (ed), GEOLOGY OF ASBESTOS DEPOSITS, Society of Mining Engineers, 1981.
7. World Health Organization, ASBESTOS AND OTHER NATURAL MINERAL FIBRES, Environmental Health Criteria 53, 1986.