|
Environmental Light Microscopy
"Environmental Light Microscopy", as addressed here, involves the analysis of
particles from an environment in order to identify the presence of a hazard
to equipement, a product, or to a life form, including humans; to identify
the sources of particles at a particular location; or to address other
concerns regarding particles at a specific location. The sample to be
analzed may be a colection of free particles or a tapelift of particles in a
fixed adhesive. Tapelifts that use an adhesive that is easily disolved is
treated as a sample of free particles.
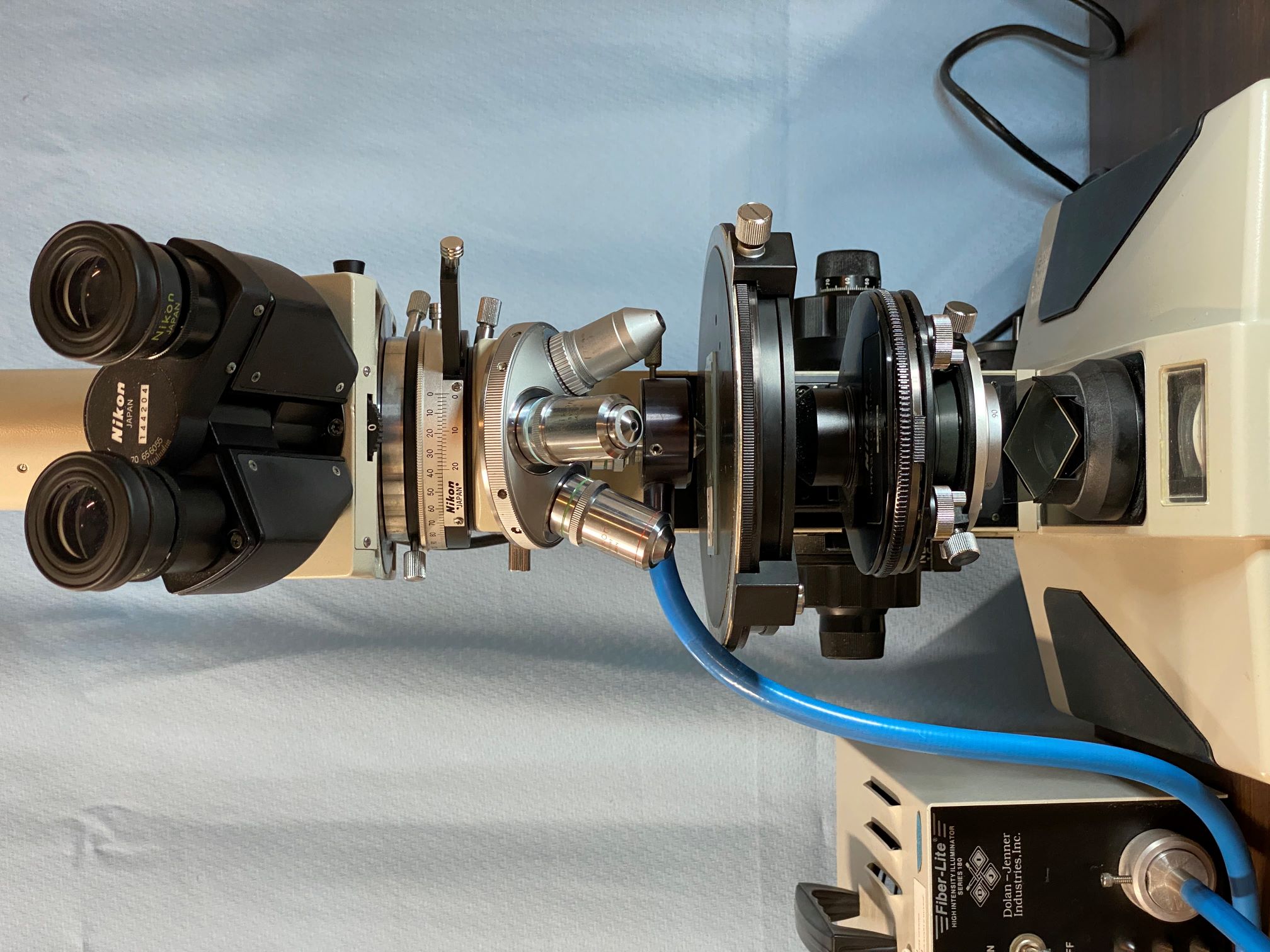
Environmental Light Microscope
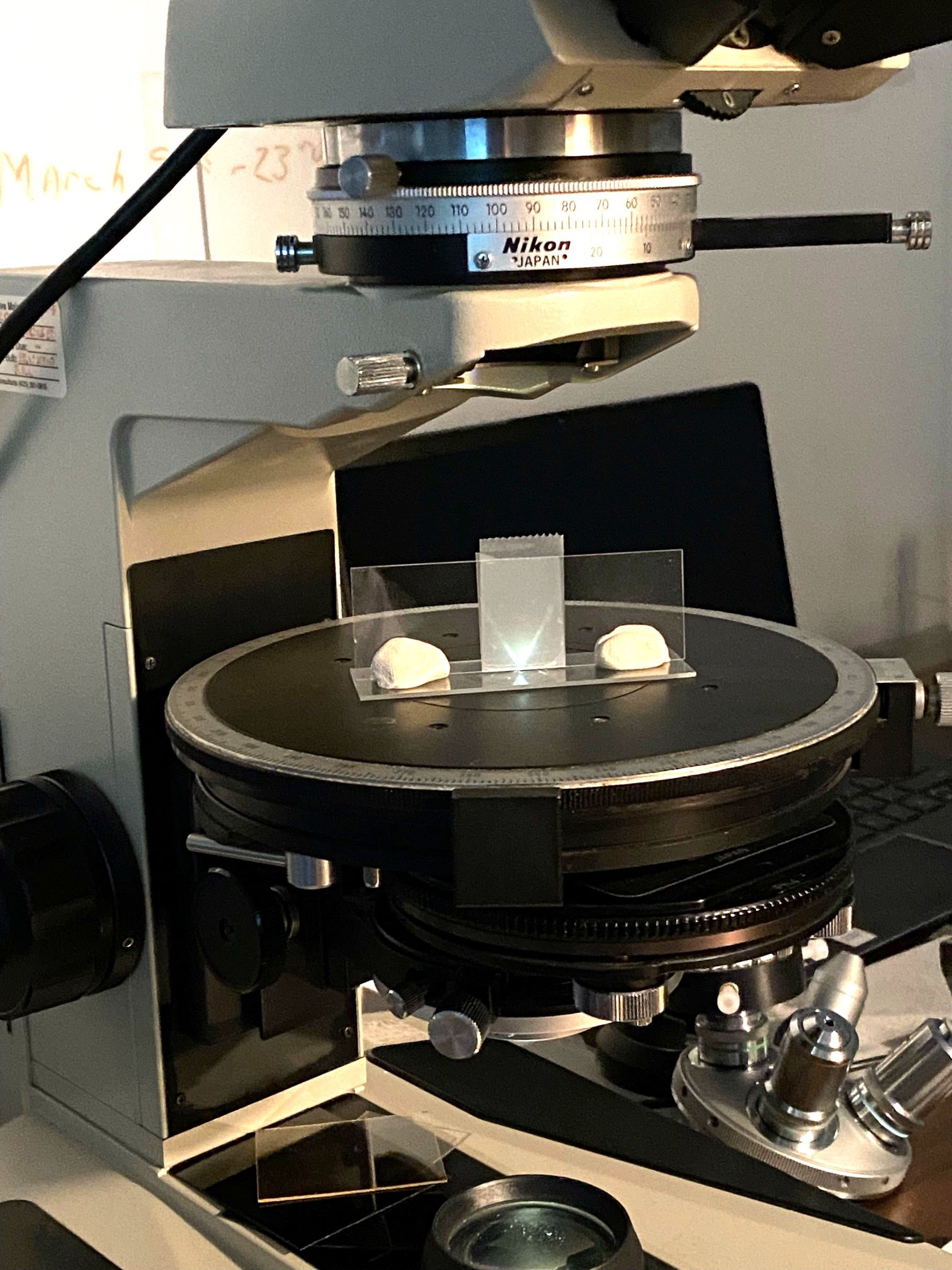
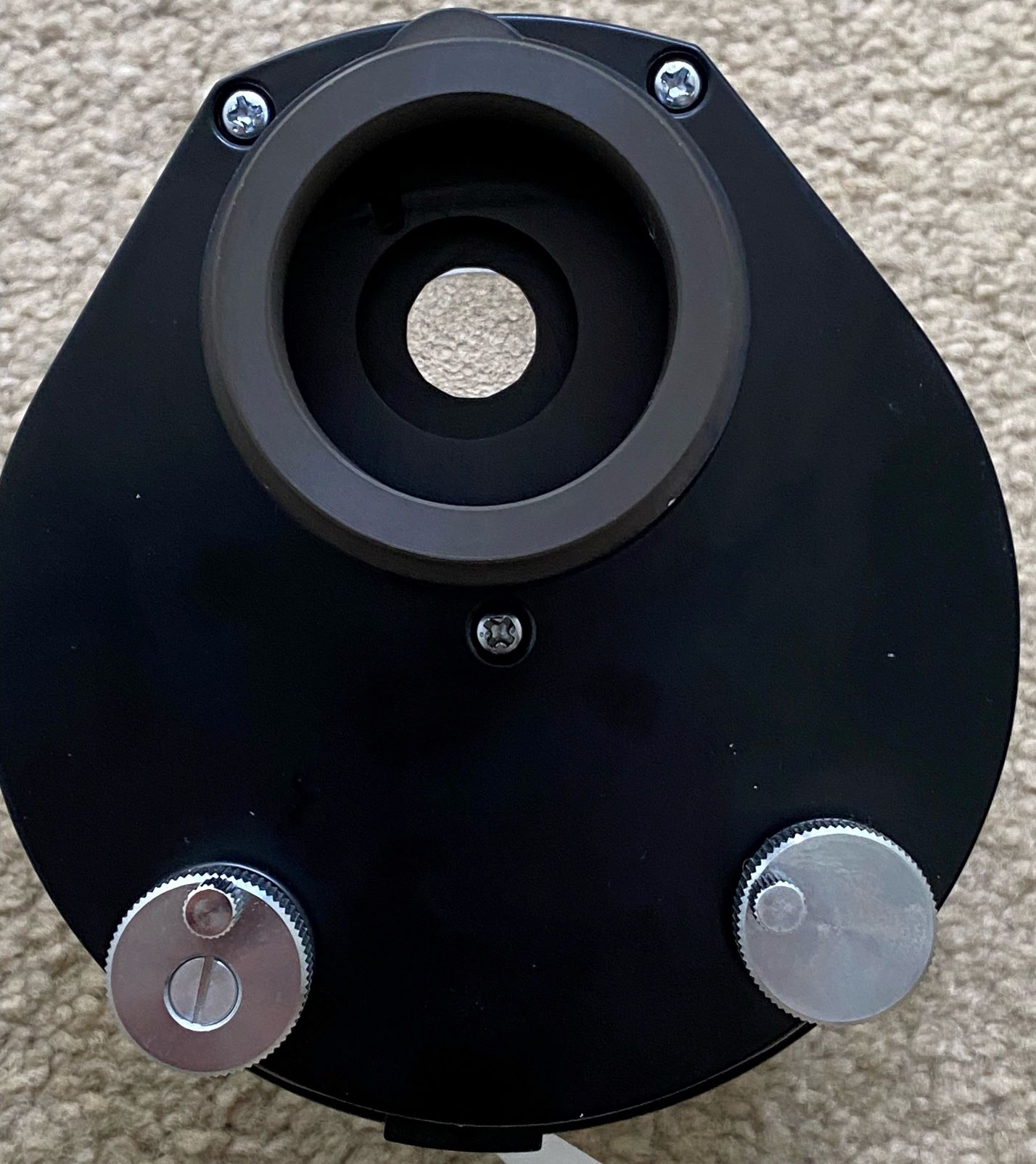
The microscope described here is one possible configuration. This example
uses a Nikon Labophot Pol scope as the base unit with an Abbe Phase Contrast
turret condenser and a ring-light epi-illuminator (image 1). The
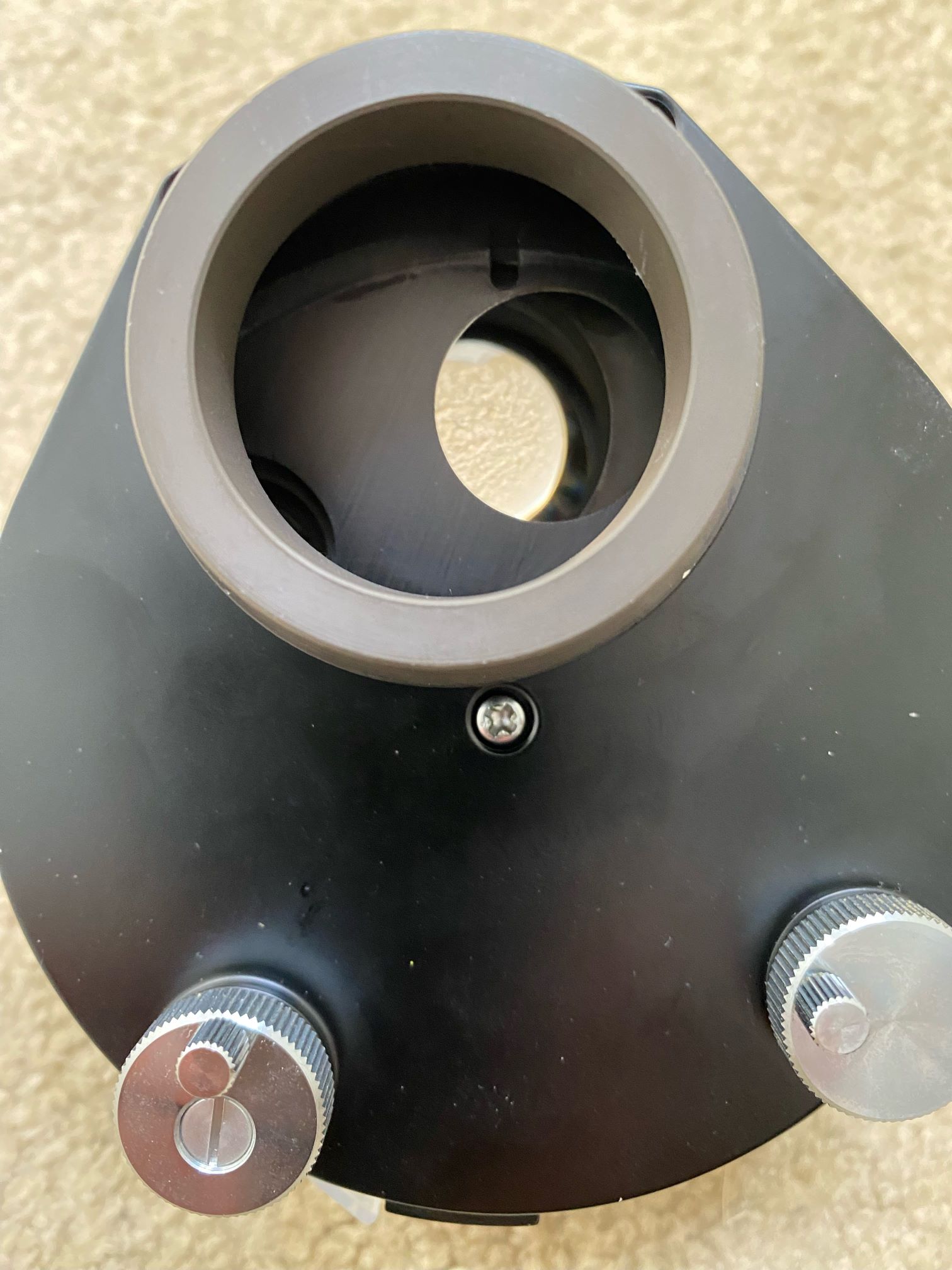
illumination light path through the particle will be shown with a frosted
slide in the position of the particle (image 2).

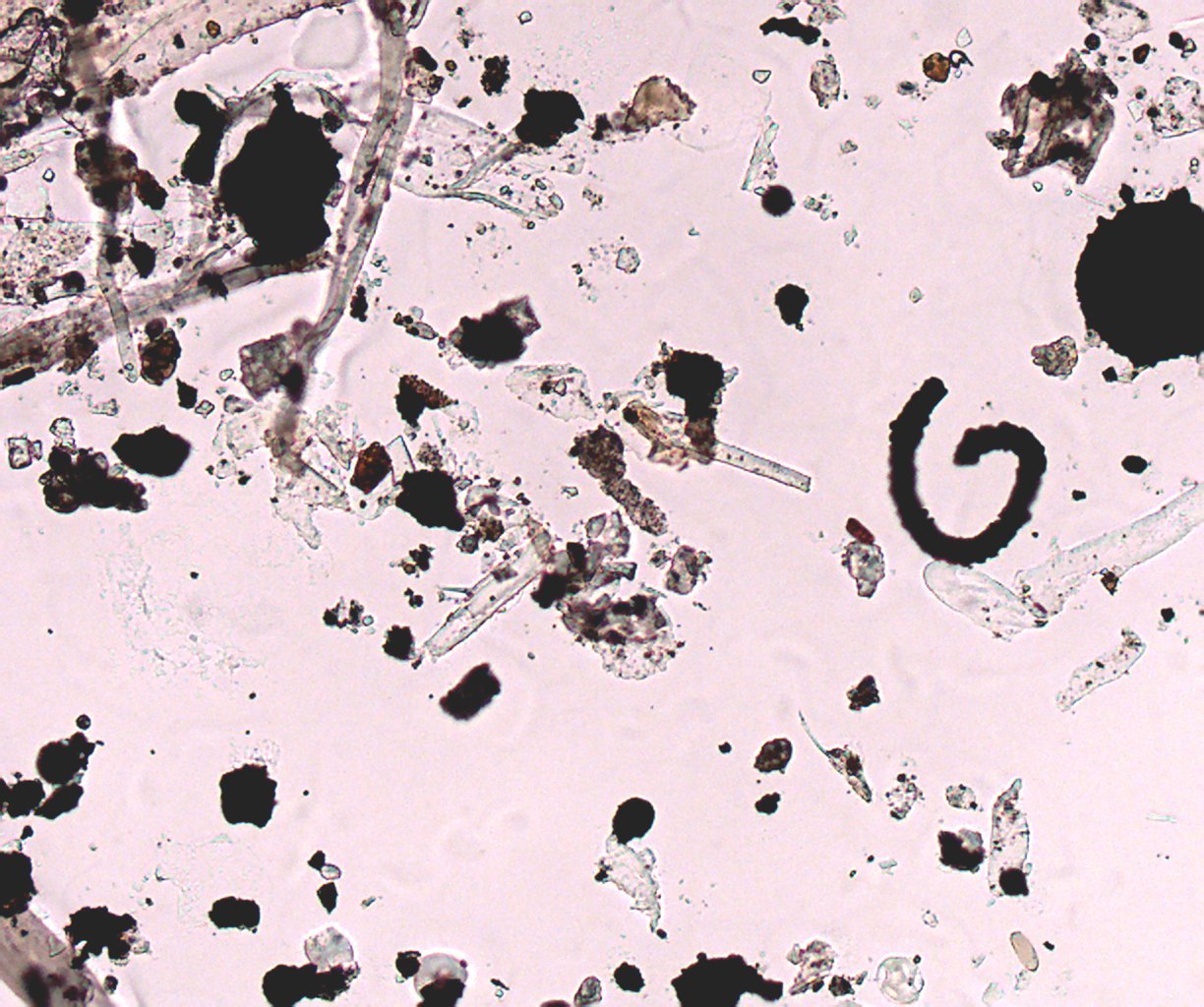
Axial illumination using the phase contrast condenser in the "0" position
with the substage iris clossed down.
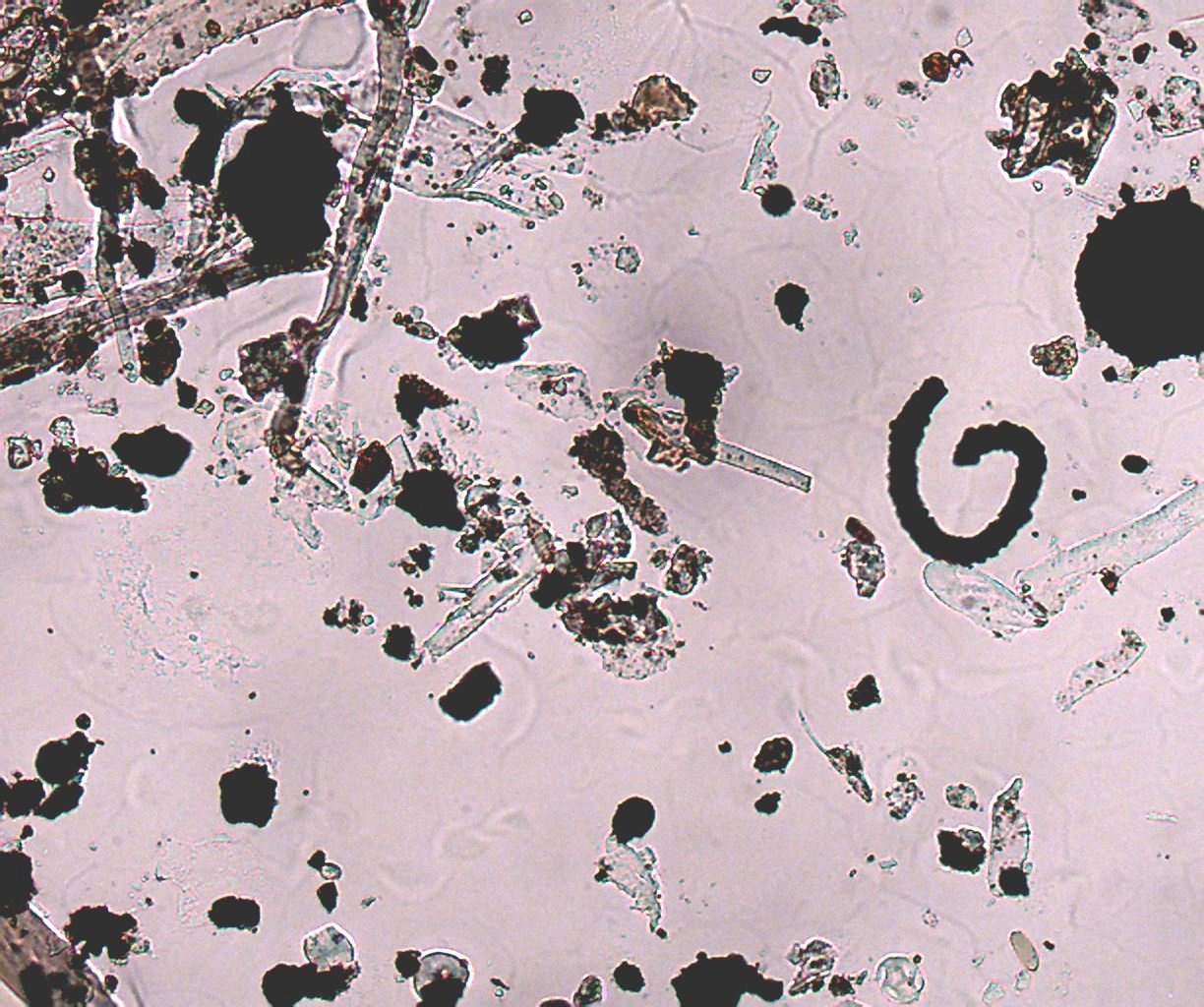




Transmitted Brightfield Illumination using the phase contrast condenser in
the "0" position with the substage iris open 2/3rds.



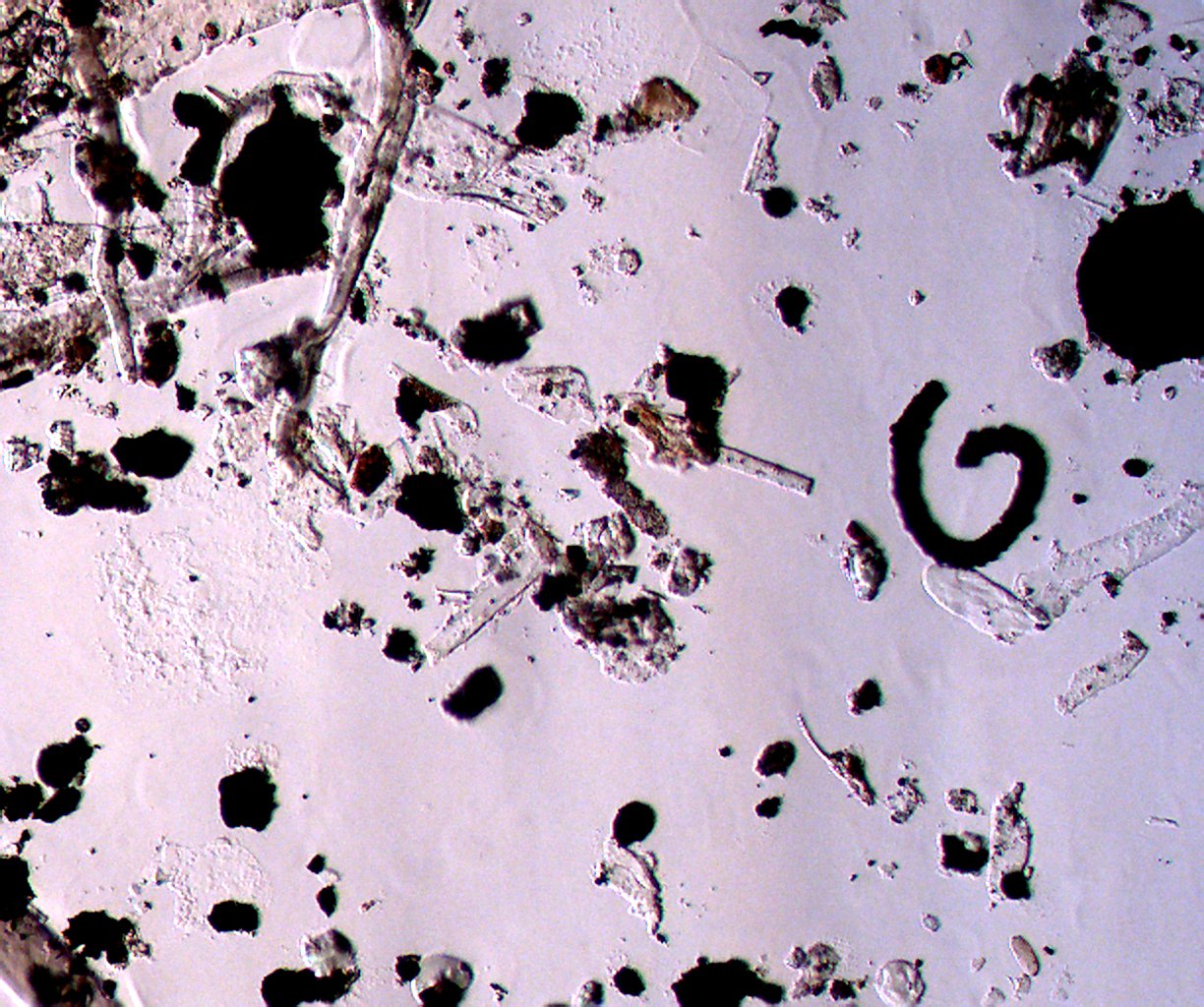
Transmitted Oblique Illumination using the phase contrast condenser in the
"Off 0" position with the substage iris wide open.
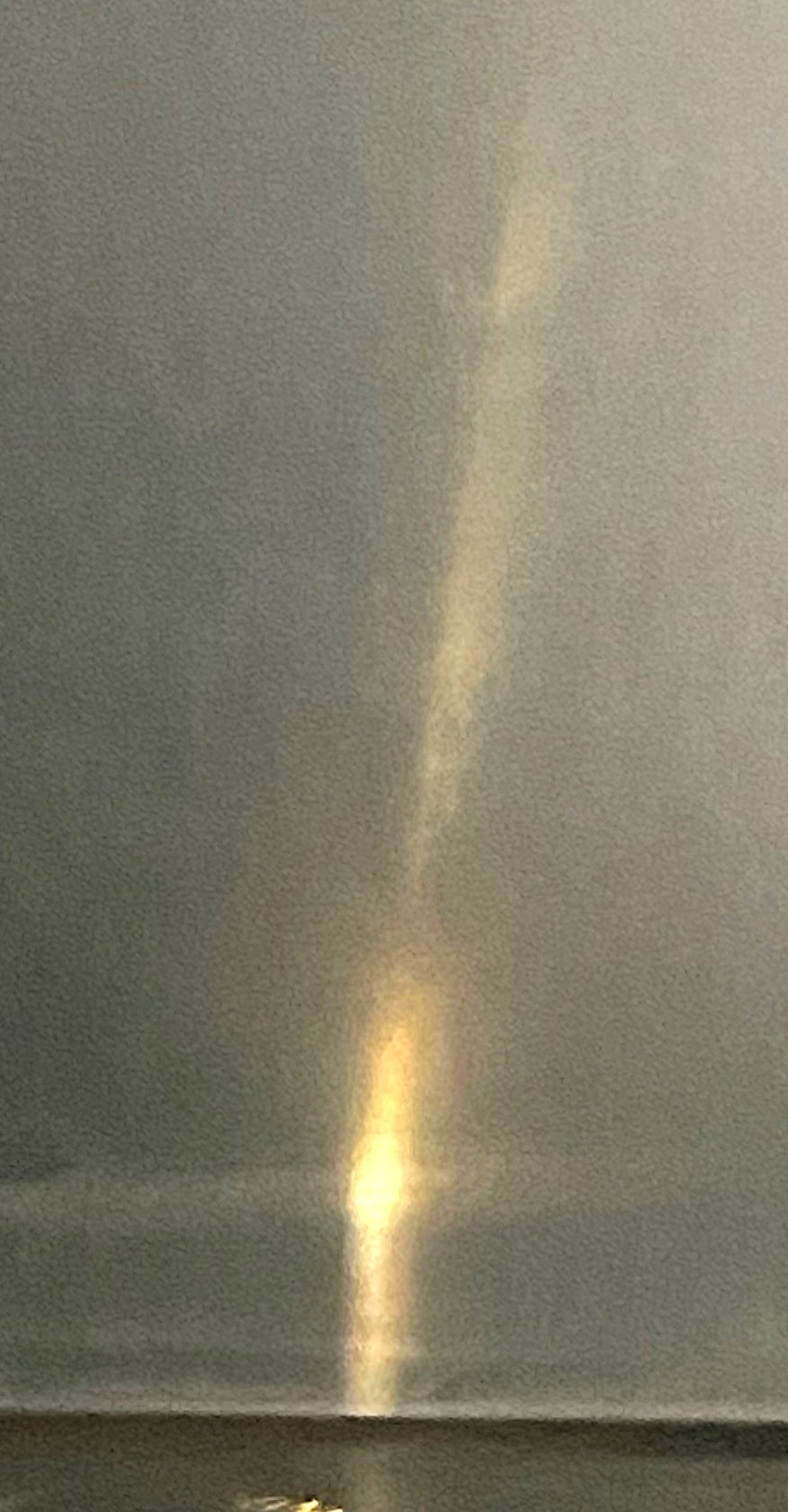



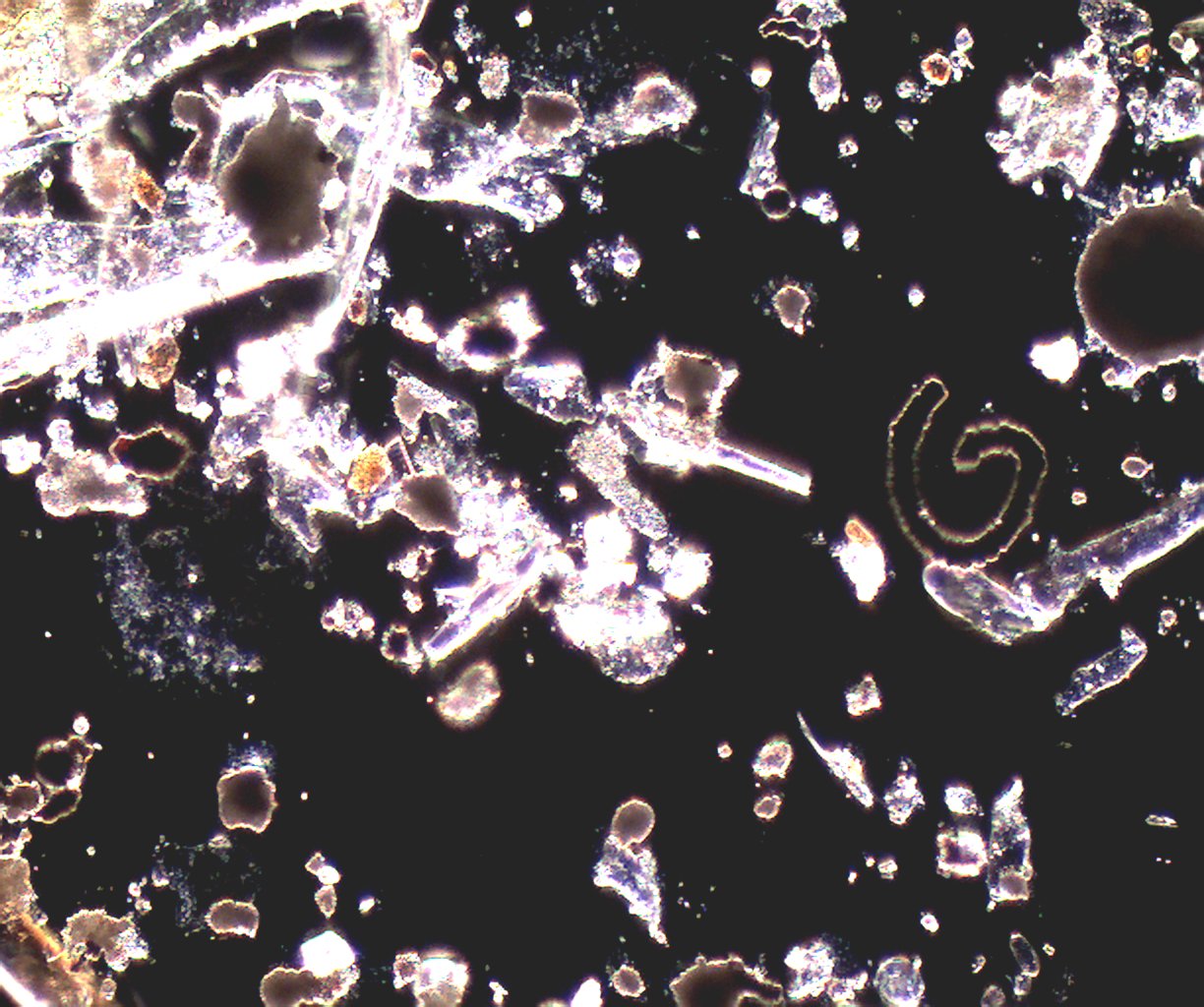
Transmitted Darkfield Illumination using the phase contrast condenser in the
"PH4" position with the 20X objective.
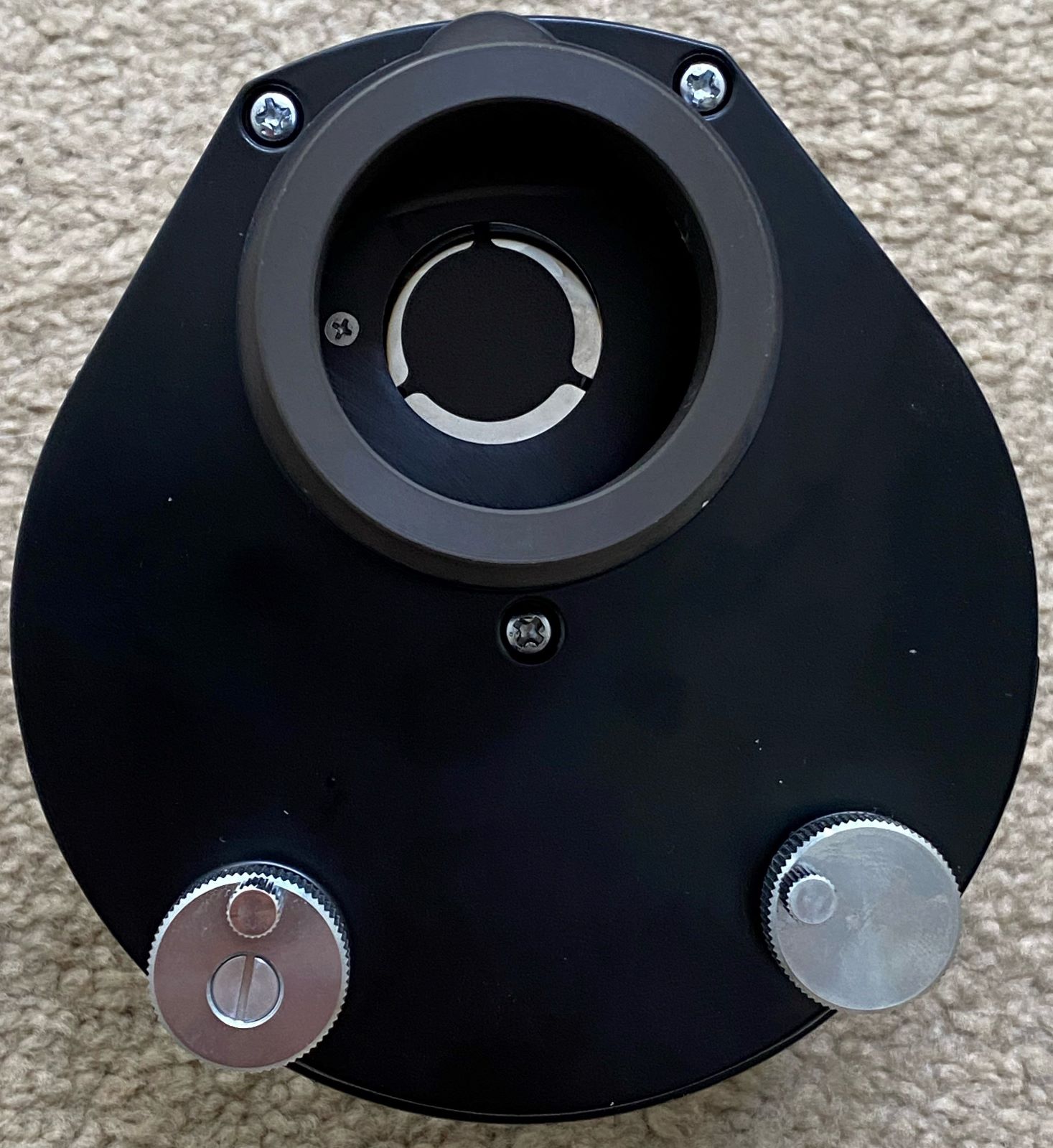
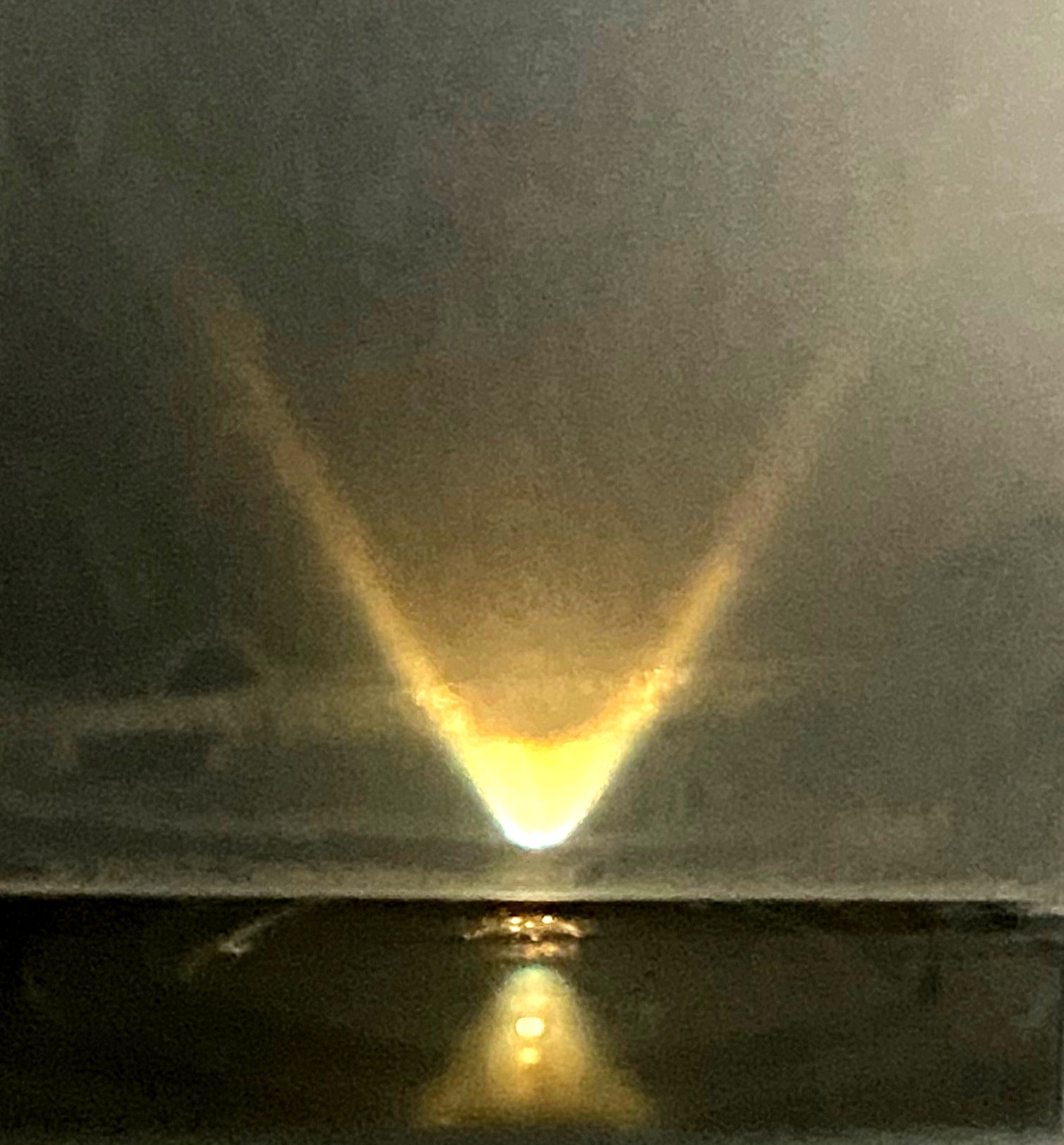






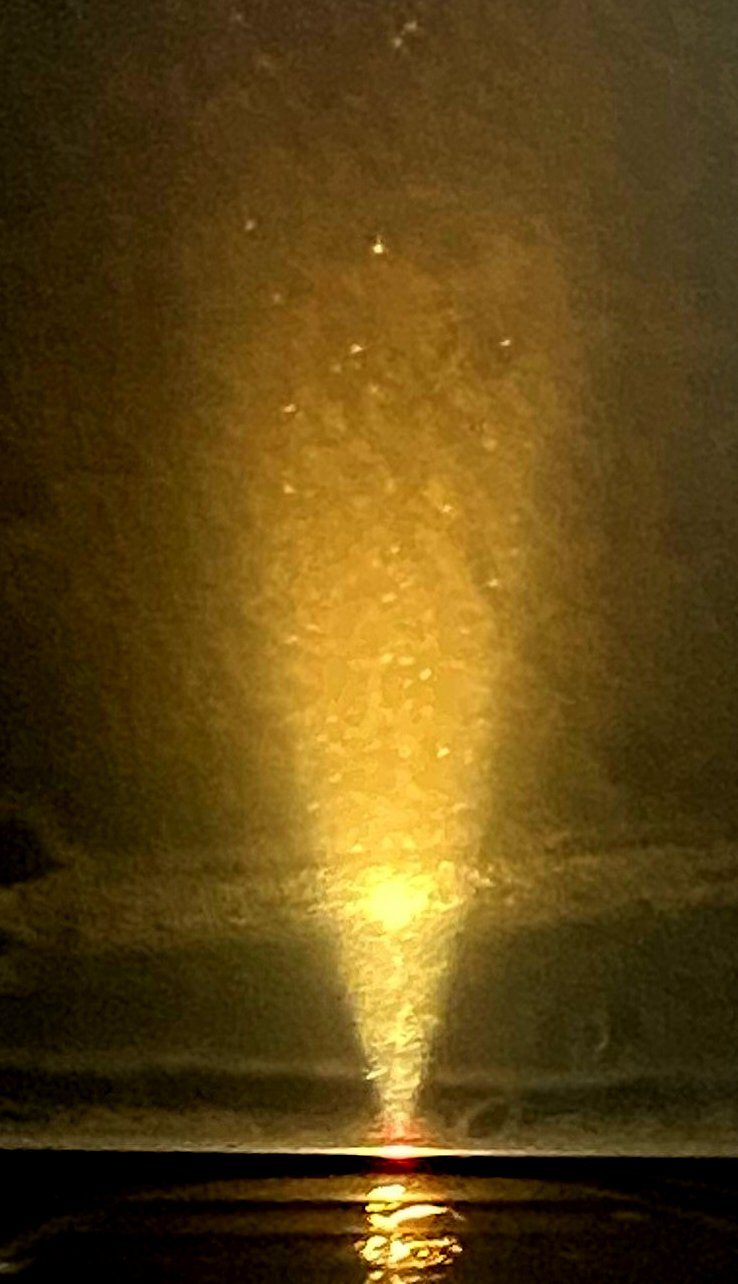
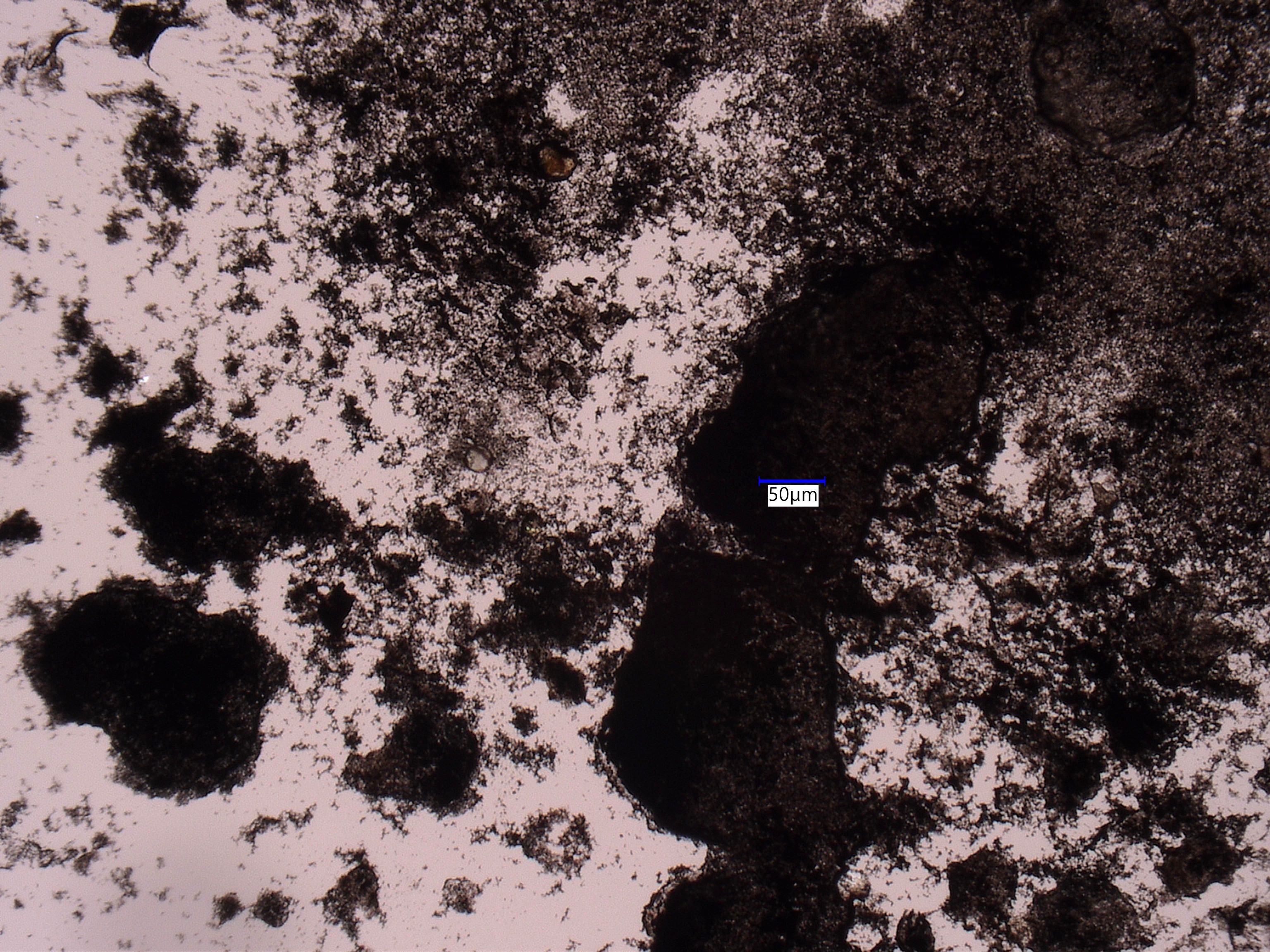
Reflected Darkfield Illumination with a ring-light accessory.
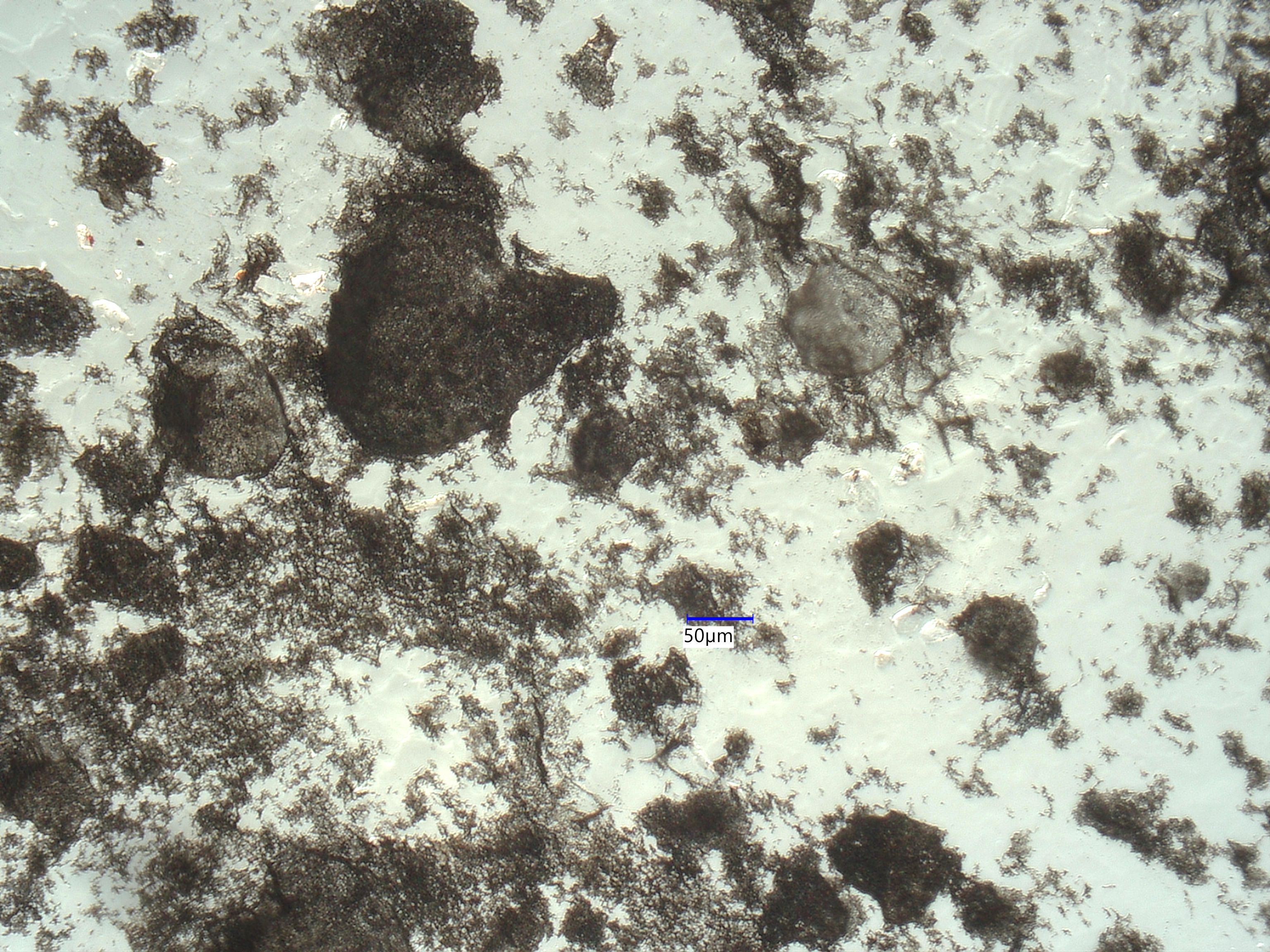

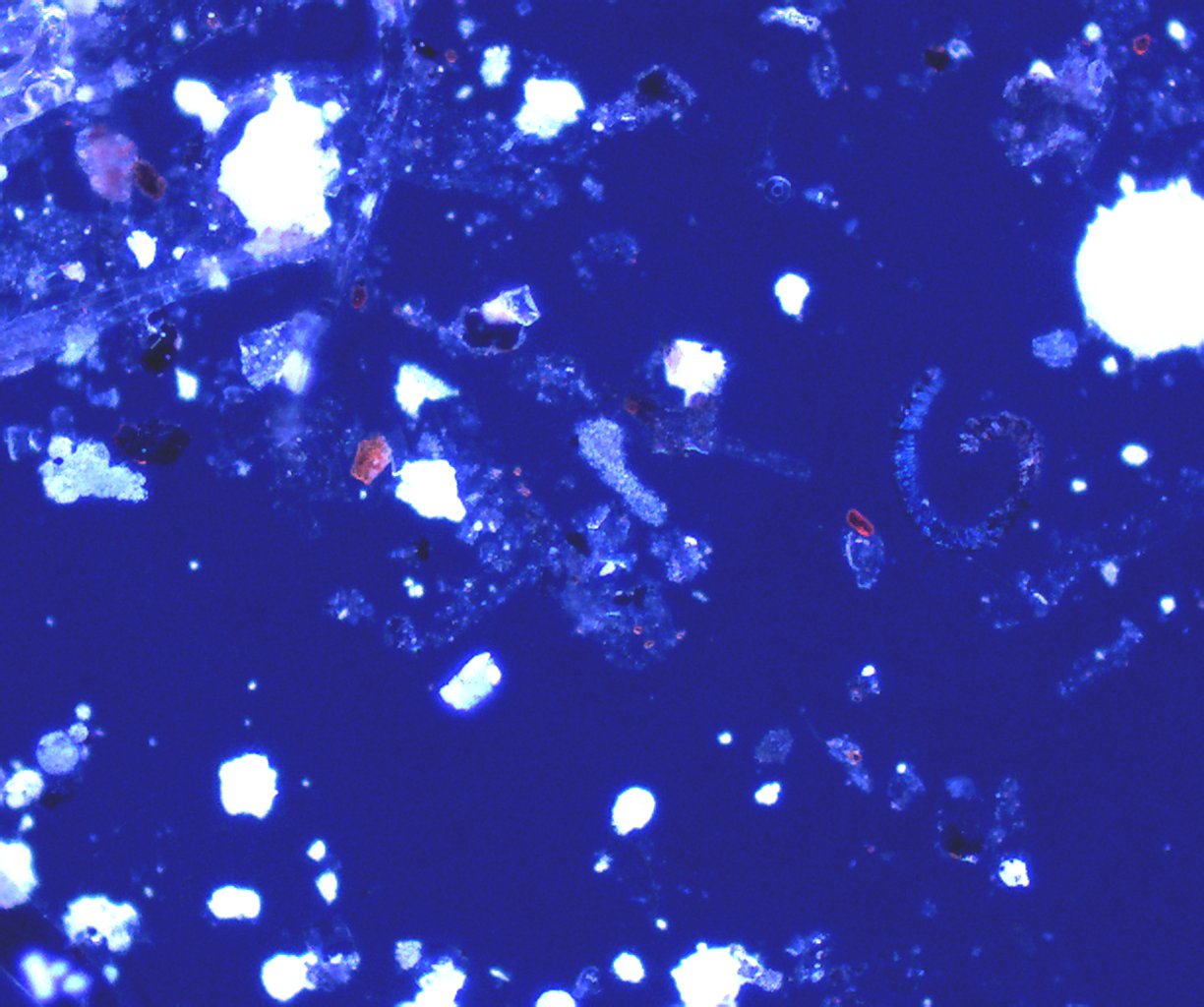
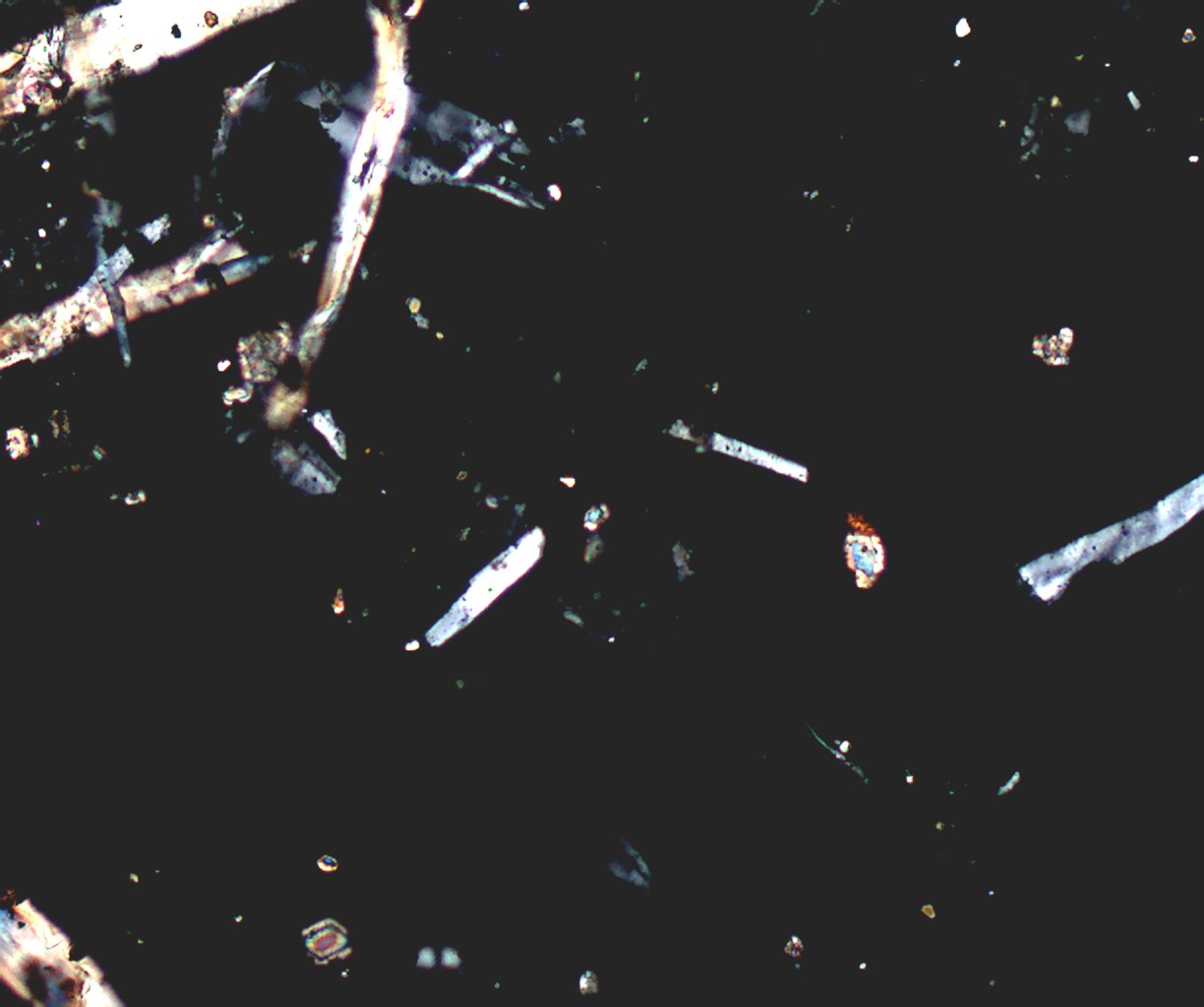
Polarized Light
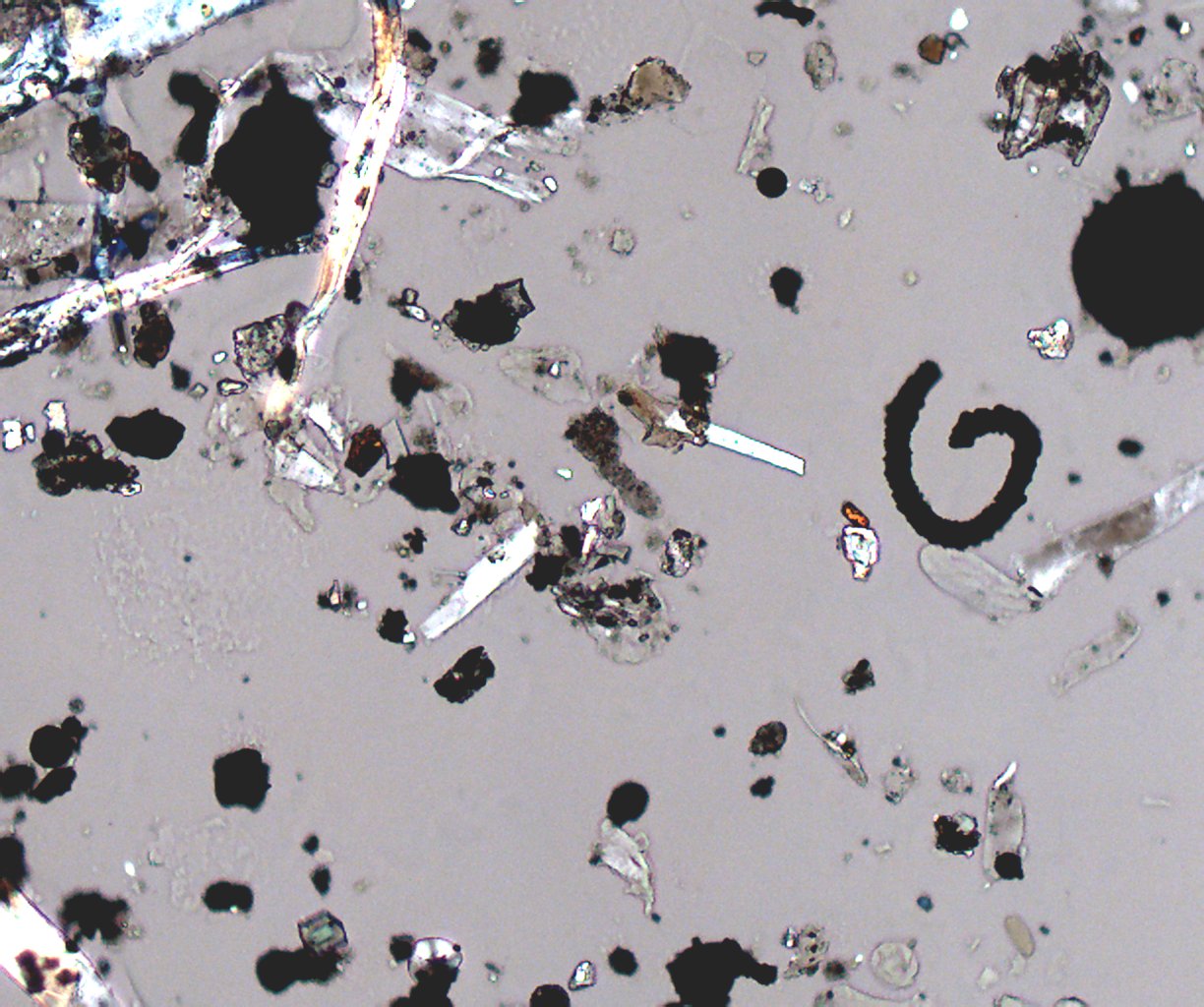
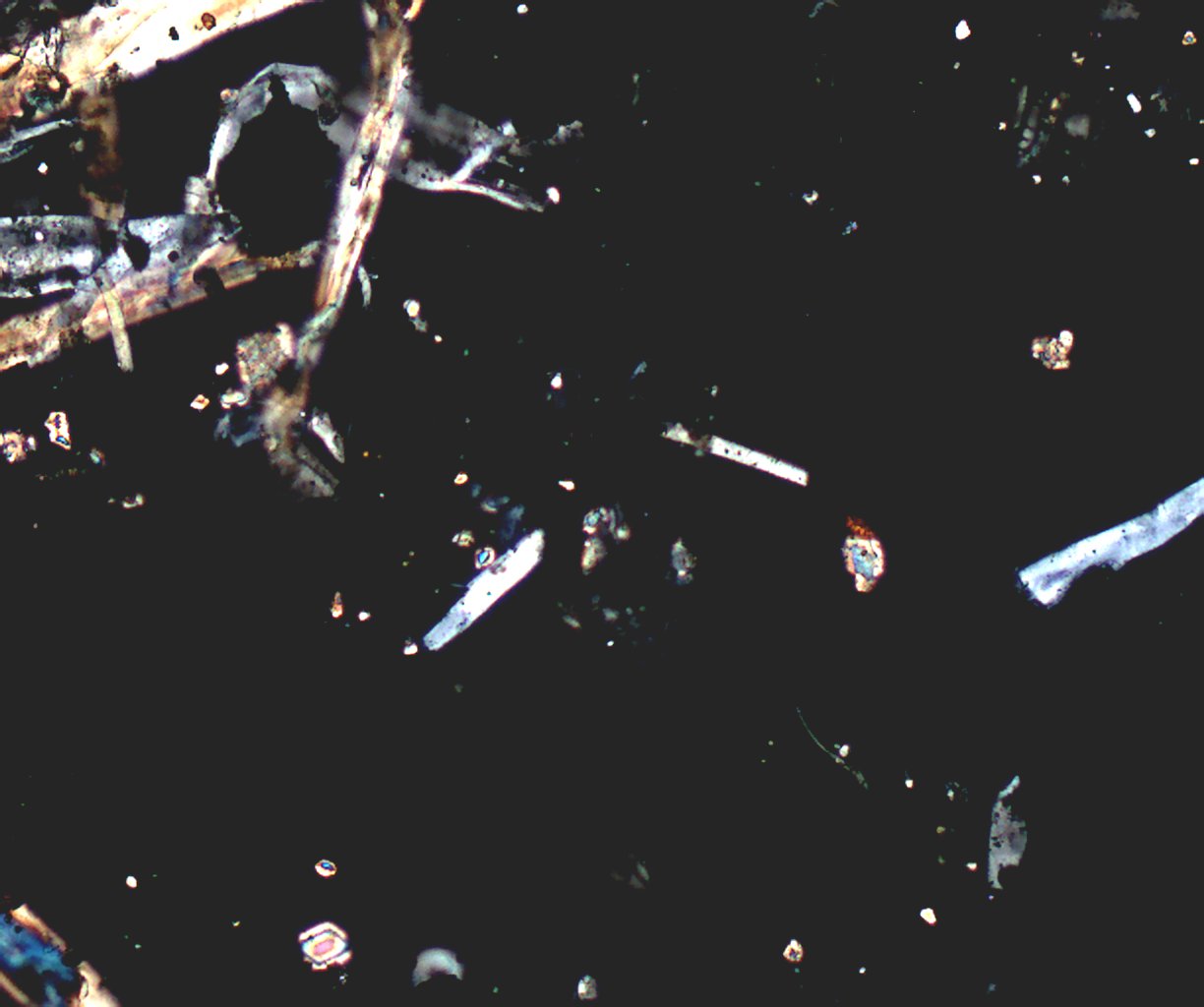
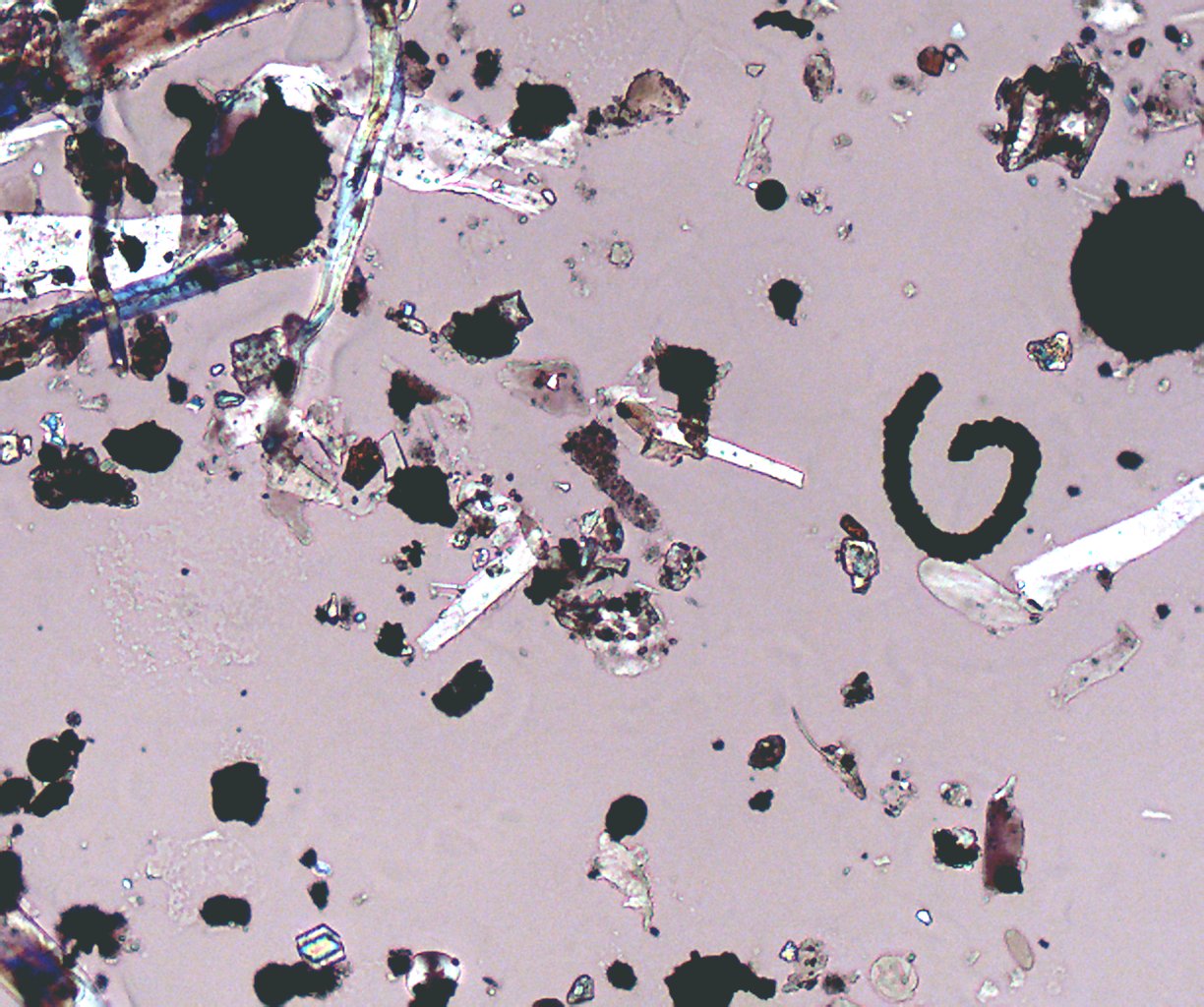



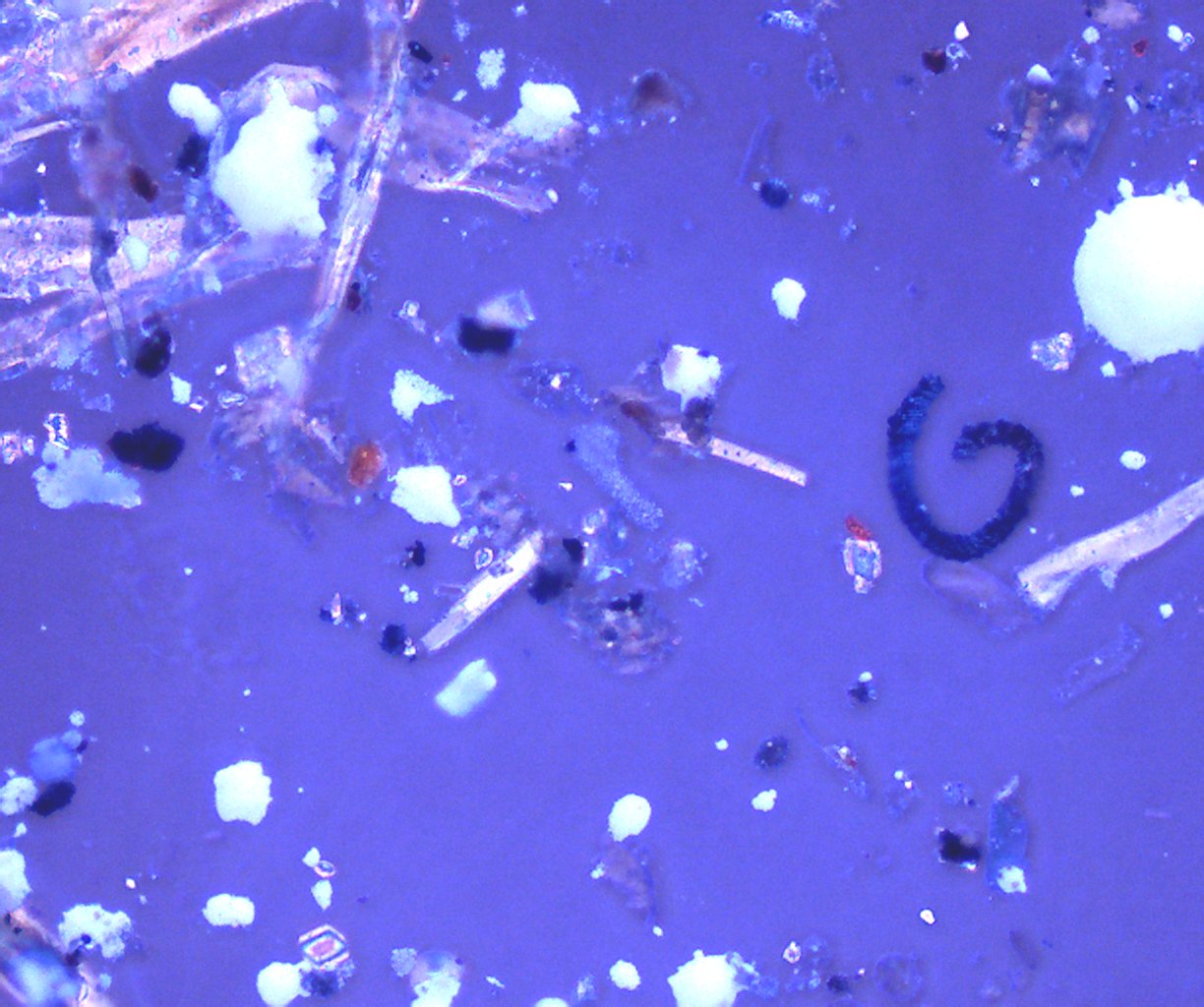
Transmitted Polarized Light with Reflected Darkfield

References
1. Crutcher, Russ and Heidie Crutcher, “What We See Part 1: Morphological
Properties of Particles in a Fixed Mountâ€, THE MICROSCOPE, vol. 70, no. 1, pp.
22-34, 2023.
2. Crutcher, Russ and Heidie Crutcher, “What We See Part 2: Physio-Chemical
Properties of Particlesâ€, THE MICROSCOPE, vol. 70, no. 2, pp. 64-81,
2023.
3. Crutcher, Russ and Heidie Crutcher, “What We See Part 3: Interfacial
Properties of Particles in a Fixed Mountâ€, THE MICROSCOPE, vol. 70, no. 3, pp.
113-126, 2023.
|