|
Terminations
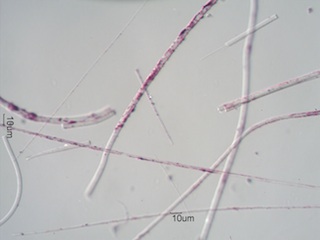
Terminations are characteristics of elongated structures or structures with
at least one set of parallel sides.
. . . Minimum Area
Brittle materials or materials with no significant tensile strength tend to
break with minimal new surface area created.
That is also dependent on the orientation of the applied force relative to
the long axis or the material. Bending creats
a tensile force on one side and a compresive force on the other.
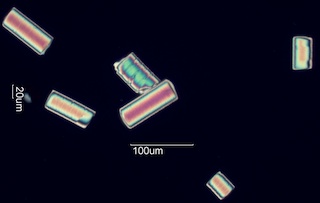
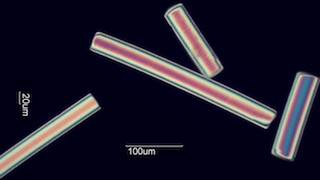
. . . Cleavage
. . . Plastic
Surfaces deform inellastically before failing
. . . Brittle
Surfaces show no evidence of plastic deformation before failure.

. . . Broomed
Broomed terminations can be the result of high tensile strength and low
compresive strength, as in the case with asbestos, or
degradation of structures holding fiber bundles in place, as in the case of
damage to the cuticle of hair.



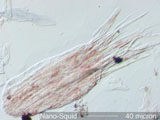
. . . Splintered
High tensile strength and relatively low compresive strength can result in
splintered terminations. Asbestos and wood are two
common examples.


. . . Melt
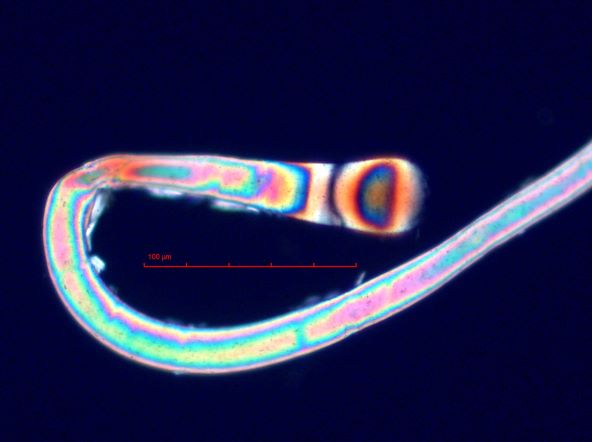
. . . Pointed
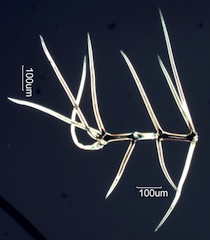


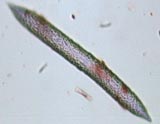
. . . Other
Hairs often have both the attachment termination and the distal termination,
often tapered. Human hair may show a rounded termination as a result
of growth after cutting (Nano-Squid, not really).
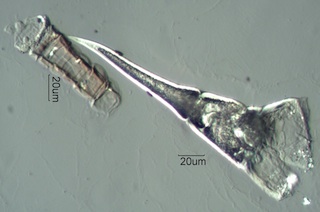


Terminations can be complex when they are the result of abrasion

|